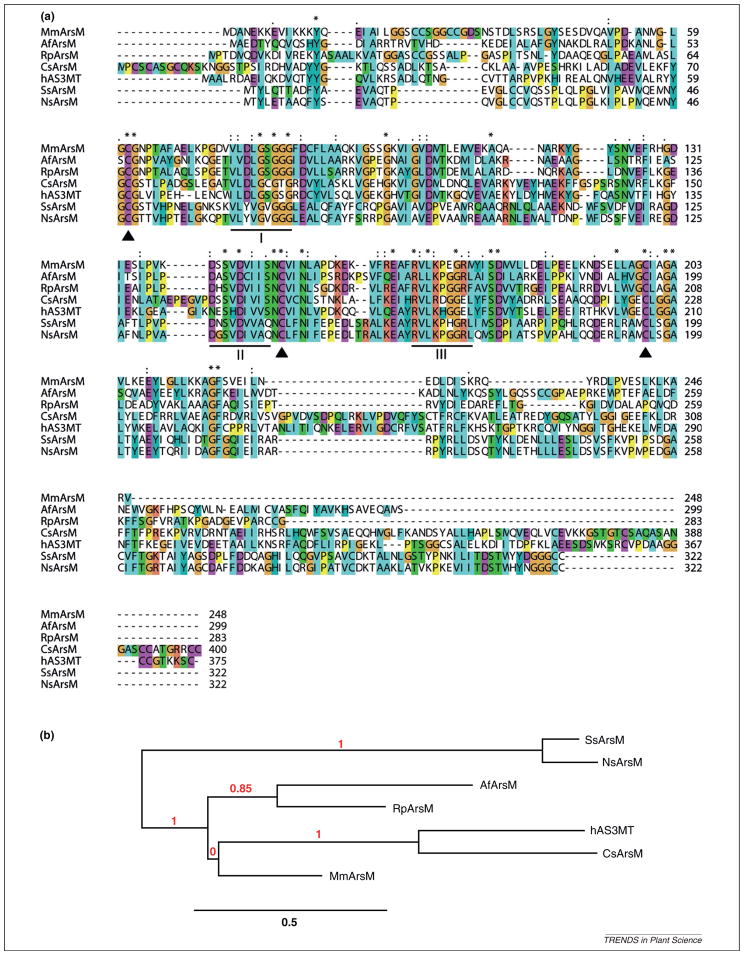
Figure 1.
Relationships of the arsenite methyltransferases (ArsM) from different species. (a) Multi-sequence alignment of ArsMs. Conserved cysteines are indicated by solid triangle. Motifs I, II and III are underlined and are involved in interactions with S-adenosylmethionine (SAM). The sequences of seven species are (species names are given in parentheses): AfArsM (Aspergillus fumigatus A1163); Czars (Cyanidioschyzon sp. 5508); hAS3MT (Homo sapiens); MmArsM (Methanosarcina mazei Go1); NsArsM (Nostoc sp. PCC 7120); RpArsM (Rhodopseudomonas palustris CGA009); and SsArsM (Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803). (b) Phylogenetic tree (produced by Phylogeny.fr [68]) comparing ArsMs.