Figure 8.
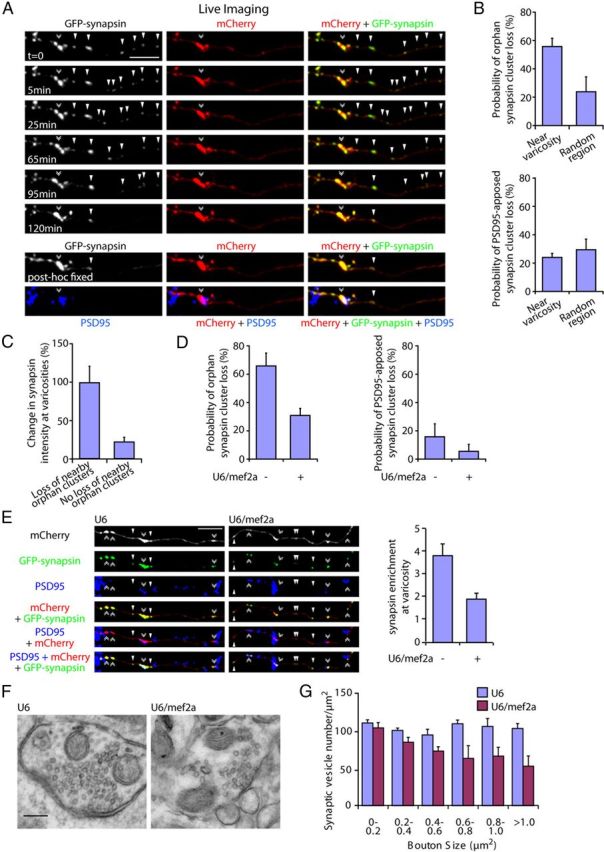
MEF2A coordinately regulates the elimination of orphan synapsin clusters and enrichment of presynaptic material at maturing presynaptic boutons. A, Granule neurons were transfected with the GFP-synapsin and mCherry expression plasmids. Live neurons were imaged using a spinning disk confocal microscope for 2 h and subjected to immunocytochemistry using the GFP, mCherry, and PSD95 antibodies. A representative image sequence is shown. Orphan synapsin clusters unapposed to PSD95 (arrowheads) are lost and coordinately synapsin enrichment is increased at the presynaptic varicosity (double arrowhead). B, Quantification of neurons transfected as in A revealed that the loss of orphan PSD95-unapposed synapsin cluster is significantly higher within a 25 μm region near presynaptic varicosities compared with that in random axon regions (top, p < 0.05, t test, n = 3). The loss of PSD95-apposed synapsin clusters near presynaptic varicosities is not significantly different compared with that in random axon regions (bottom). C, Quantification of the change in synapsin intensity at presynaptic varicosities during the imaging interval as in A. The loss of orphan synapsin clusters within a 25 μm region near presynaptic varicosities was associated with a significant increase in synapsin enrichment at presynaptic varicosities compared with that in presynaptic varicosities with no orphan synapsin cluster loss in their vicinity (p < 0.005, t test, n = 3). D, Granule neurons were transfected with the GFP-synapsin and mCherry expression plasmids together with the U6/mef2a, or control U6 RNAi plasmid and analyzed as in B. Knockdown of MEF2A reduced the loss of orphan PSD95-unapposed synapsin clusters (left, p < 0.01, ANOVA followed by Fisher's PLSD post hoc test, n = 3), but not synaptic PSD95-apposed synapsin clusters, near presynaptic varicosities (right). E, Granule neurons were transfected with the GFP-synapsin and mCherry expression plasmids together with the U6/mef2a or control U6 RNAi plasmid and subjected to immunocytochemistry using the GFP, mCherry, and PSD95 antibodies. Left, Representative images of knockdown and control neurons are shown. Right, Quantification of the intensity of synapsin at presynaptic varicosities normalized to the intensity of synapsin at orphan PSD95-unapposed presynaptic sites. Depletion of MEF2A reduced the enrichment of synapsin at presynaptic varicosities (p < 0.05, ANOVA followed by Fisher's PLSD post hoc test, n = 3). Scale bar, 10 μm. F, Representative presynaptic boutons from control or MEF2A knockdown granule neurons subjected to electron microscopy analyses. Presynaptic boutons contain synaptic vesicles and mitochondria, and are apposed to postsynaptic densities. G, Quantification of synaptic vesicle number in presynaptic boutons normalized to bouton size from control or MEF2A knockdown neurons as in F. Depletion of MEF2A significantly decreased synaptic vesicle number in larger boutons with an area of 0.6–0.8 μm2 (p < 0.01, ANOVA followed by Fisher's PLSD post hoc test, n = 3), 0.8–1.0 μm2 (p < 0.05, ANOVA followed by Fisher's PLSD post hoc test, n = 3), and >1.0 μm2 (p < 0.005, ANOVA followed by Fisher's PLSD post hoc test, n = 3), but not in boutons smaller than 0.6 μm2. Scale bar, 200 nm.
