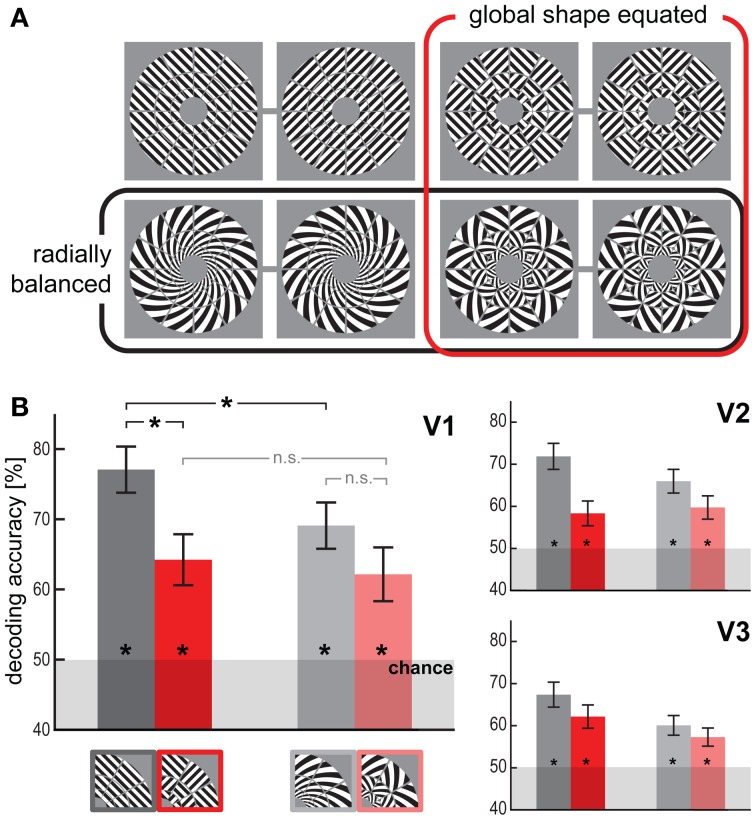
Figure 1.
Visual orientations are robustly decodable for all stimulus types. (A) The four stimulus types, uniform gratings (upper left pair), spirals (lower left pair), patch-swapped gratings (upper right pair), and patch-swapped spirals (lower right pair). For each type we presented two differently oriented exemplars (pairing indicated by gray lines) with a 90-deg orientation disparity at every location. Stimuli were presented centered on fixation. The retinal diameter of each stimulus was 14.08° (inner-border radius: 1.5°, outer-border radius: 7.04°). (B) Orientation decoding accuracy (linear SVM, leave-one-subrun-out cross-validation) for each stimulus type and visual area (V1-3). Error bars indicate the standard error of the mean across all 18 subjects. Asterisks on bars indicate that decoding accuracy was significantly above chance level (p < 0.01). Asterisks on horizontal brackets indicate significant differences (p < 0.05) between decoding accuracies.