Figure 2.
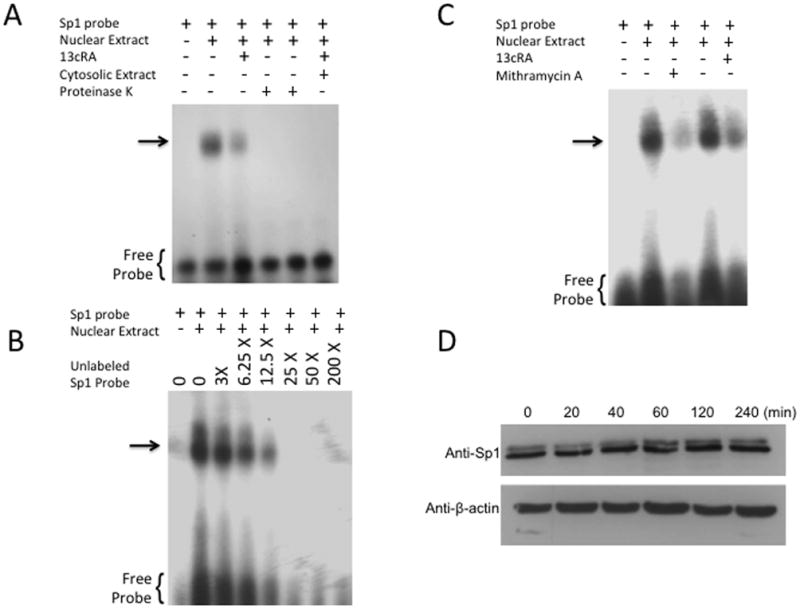
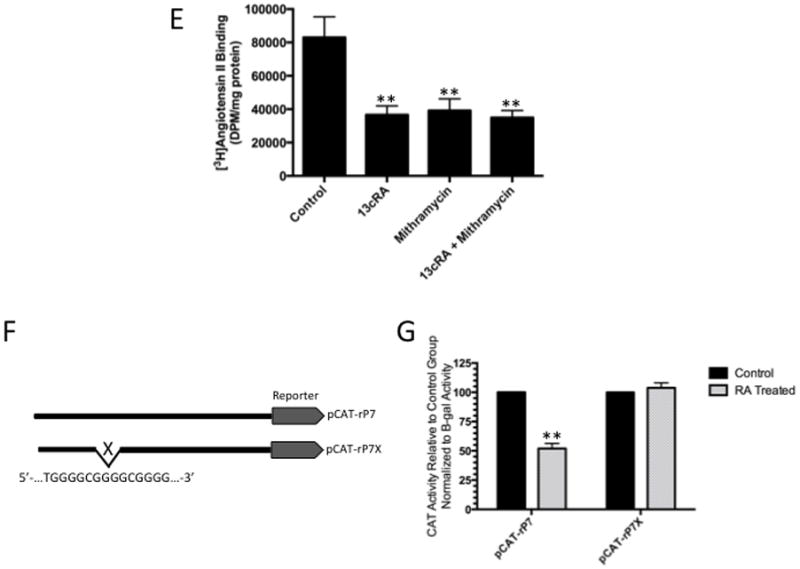
Identification of specific protein binding activity in WB nuclear extracts to Sp1RE. To identify protein binding to Sp1RE in 13cRA treated WB nuclear extracts, mobility shift assays were performed. 32P-labeled Sp1 probe was incubated with 10 μg of nuclear or cytosolic extracts. Samples were analyzed on 6% non-denaturing polyacrylamide gels and visualized by autoradiography. The position of the protein-DNA complex is indicated by arrow. (A) Labeled probe in the absence of nuclear or cytosolic extract (lane 1), in the presence of untreated nuclear extract (lane 2), in the presence of 13cRA exposed nuclear extract (lane 3), nuclear extracts of both untreated and treated with 13cRA in the presence of proteinase K (lanes 4 and 5), and in the presence of cytosolic extract (lane 6). (B) Mobility shift assay performed using labeled Sp1RE in the presence of increasing concentrations of unlabeled Sp1RE probe as indicated. The position of the protein-DNA complex is indicated by arrow. (C) Mobility shift assay of nuclear extracts treated with 13cRA or mithramycin A, both showing significant reduction in protein binding activity. (D) Time course 13cRA treatment Western blot analysis of Sp1 protein within the time-frame in which EMSA analysis was conducted reveals no significant change in Sp1 expression, p>0.05, n=3. (E) [3H]AngII binding assay demonstrating significant reduction in AngII binding in 13cRA, mithramycin A, and 13cRA + mithramycin A conditions (**p<0.01, n=3). (F) Schematic representation of the pCAT reporter expression vector unaltered rP7 portion of rat AT1R gene or modified mutant lacking indicated Sp1 response element. (G) Solid bars represent the CAT activity of control plasmids, the value set automatically at 100% activity relative to β-galactosidase co-transfection control, patterned bars represent the comparative CAT activity in 25 μM 13cRA treated cells. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM, **p<0.01, n=3.
