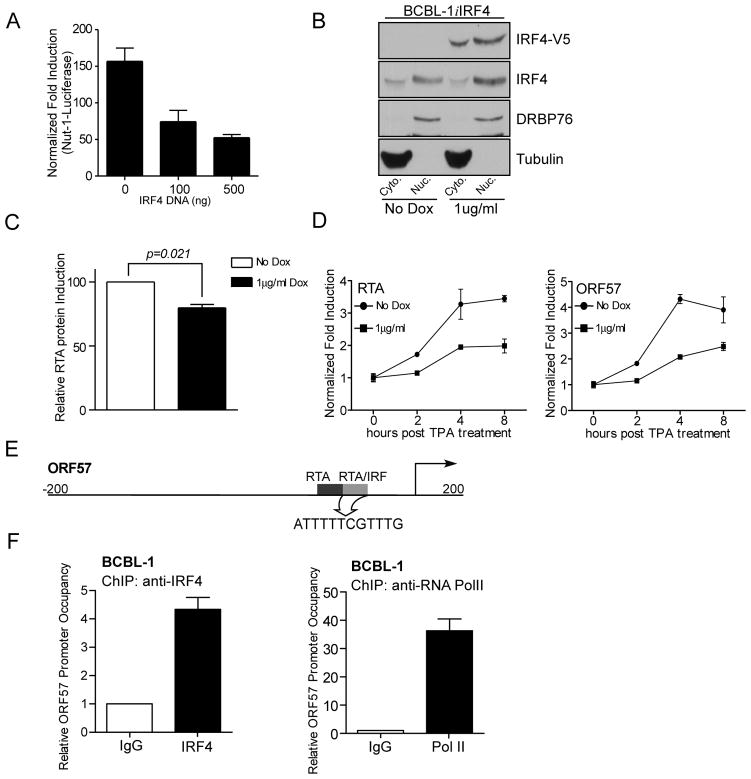
Figure 7. IRF4 inhibits KSHV viral reactivation.
(A) Effect of IRF4 on Nut-1 luciferase in 293T cells. 293T cells were co-transfected with 100 or 500 ng of IRF4 expression plasmid, 0.4 μg Nut-1 luciferase reporter construct, 24ng pRL-Null and either 75 ng of RTA cDNA or empty vector. Total transfected DNA levels were kept equal with empty vector. 48 h after transfection, luciferase activity was measured. Fold induction was normalized to both Renilla luciferase activity and non-RTA transfected cells.
(B) Analysis of IRF4 protein expression levels in BCBL-1iIRF4 cells. 2×105 cells/ml BCBL-1i4 cells were treated with 1 μg/ml Dox or left untreated for 48 hrs. Subcellular fractions were harvested as previously described and subjected to immunoblot with anti-RTA antibody.
(C) Ectopic IRF4 expression leads to reduced RTA protein expression. 2×105 cells/ml BCBL-1iIRF4 cells were treated with 1 μg/ml Dox or left untreated for 48 h, followed by stimulation with 15ng/ml TPA or DMSO for 12 h prior to harvesting. Cell lysates were subject to immunoblot with anti-RTA antibody. RTA expression levels were quantified for three independent experiments and induction was calculated relative to cells without Dox stimulation.
(D) Inhibition of RTA and ORF57 mRNA induction in BCBL-1 cells by IRF4. BCBL-1iIRF4 cells were stimulated with doxycycline for 48 h followed by stimulation with 15ng/ml TPA for 2, 4, and 8 h. Fold induction of RTA mRNA levels were normalized to RPL32 and non-TPA stimulated cells.
(E) Schematic representation of the ORF57 promoter-regulatory region depicting position of RTA binding sites (black) and the RTA/IRF binding (gray). The RTA/IRF target sequence has been highlighted.
(F) Chromatin-immunoprecipitation of endogenous IRF4 bound to ORF57promoter in BCBL-1 cells. IRF4 (left) and Pol II (right) binding to the ORF57 promoter was analyzed by ChIP assay as previously described. Relative promoter occupancy was determined relative to isotype control antibody (value 1).