Fig. 2.
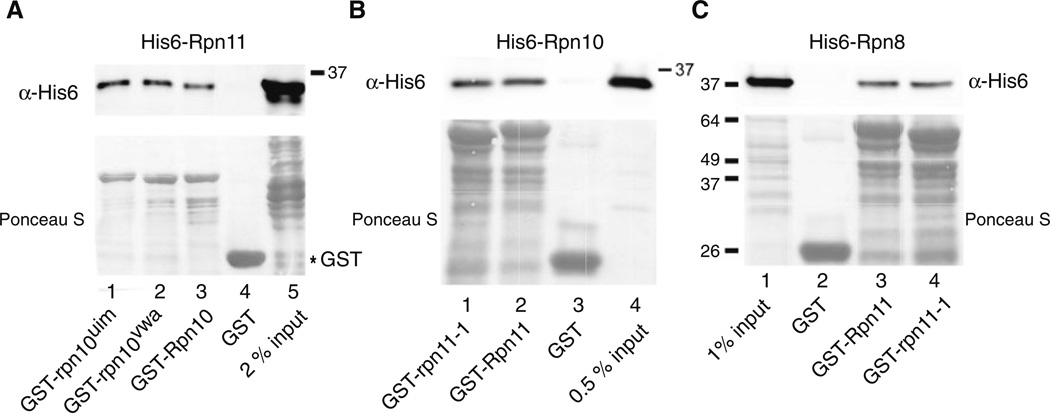
Well-characterized mutants do not affect Rpn10/Rpn11 interaction in vitro. a Rpn10 and mutant derivatives rpn10uim and rpn10vwa, were expressed as fusions to GST, purified from E. coli, and immobilized on glutathione-Sepharose beads. His6-Rpn11 was incubated with the beads, and interaction was determined by immuno-blotting. The upper panel shows interaction of His6-Rpn11 with the Rpn10/rpn10 proteins, and the lower panel shows the amount of GST-tagged proteins bound to the affinity matrix. b In a complementary experiment, Rpn11 and rpn11-1 protein mutants were fused to GST and immobilized on glutathione-Sepharose. Interaction with His6-Rpn10 was determined by immunoblotting (upper panel). The lower panel shows the level of GST proteins on the Sepharose beads. c Because both Rpn8 and Rpn10 bind Rpn11, we investigated if the rpn11-1 mutant protein had distinct interaction patterns with another proteasome subunit (Rpn8). Binding reactions were performed as described in b