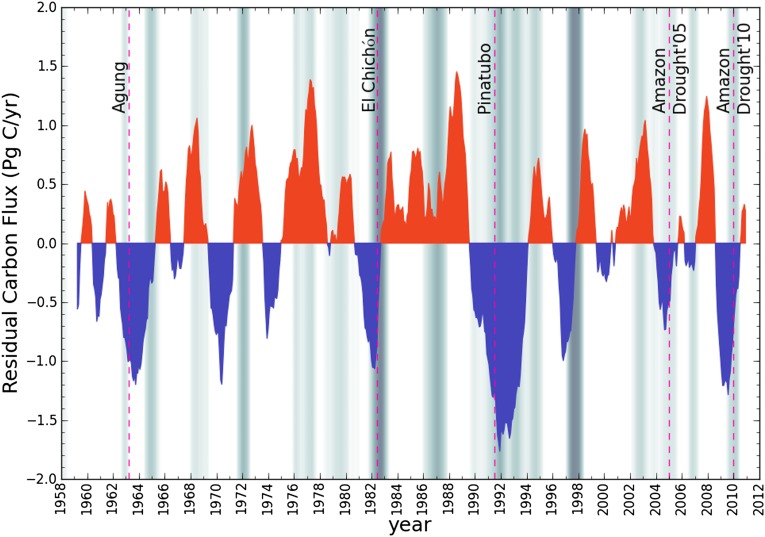
Fig. 4.
Residual carbon flux anomalies estimated by the difference between the observed atmospheric CO2 growth rate and those estimated from tropical land-surface temperature anomalies with a linear regression model. Positive values indicate carbon fluxes into the atmosphere (sources) and negative values indicate carbon fluxes into the surface (sinks). The background shading is the same as in Fig. 1. As shown, the extra carbon sink of 1990 to 1994 may have started 1 to 2 y before the eruptions of Mount Pinatubo. Therefore, it was most likely induced by multiple factors that concurred during that time (56) as detailed in the text.