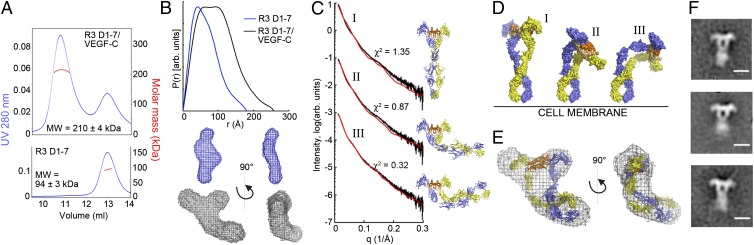
Fig. 5.
Characterization of the VEGF-C/VEGFR-3 D1-7 complex in solution and in EM. (A) MALS analysis of the VEGF-C/VEGFR-3 D1-7 complex and VEGFR-3 D1-7. (B) The SAXS-derived distance distribution functions and averaged ab initio shape reconstructions of VEGFR-3 D1-7 and the VEGF-C/VEGFR-3 D1-7 complex. (C) Rigid-body models before and after refinement against the SAXS data were aligned using VEGF-C and are shown in cartoon form. The calculated (red) and experimental scattering curves (black) are compared. (I) The symmetrical model before refinement. (II) A representative model of the refinement with limited movement: D123C dimer–linker–D45 dimer–linker–D67 dimer. (III) Representative model of the refinement with increased movement: D12C dimer–linker–D3-D3–linker–D4-D4–linker–D5 dimer–linker–D67 dimer (SI Methods). (D) Rigid-body models from C aligned using the membrane-proximal D6-7 in vertical orientation and shown in a surface representation. (E) Overlay of the ab initio model of the complex from B and the final rigid-body model from C. (F) Representative class averages of the negative stain EM analysis of the VEGF-C/VEGFR-3 ECD complex. (Scale bar: 10 nm.)