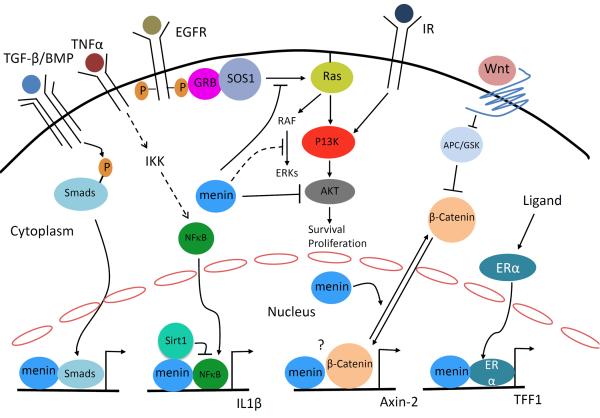
Figure 4. Menin regulates multiple signaling pathways.
Menin interacts with SMAD3 or SMAD1/5 to enhance TGFβ or BMP signaling, respectively, in various types of cells. Menin also interacts with NFκB and recruits Sirt1 to deacetylate p65 to suppress NFκB-induced gene expression. β-catenin is located in cell membrane, in presence of Wnt signaling it is translocated to the nucleus. In insulinoma cells, menin interacts with β-catenin to upregulate gene transcription, whether they associate with each other at the promoter of Axin 2 is not known. In contrast in MEFs, menin promotes nuclear export of β-catenin to suppress its transcriptional activity. Menin also interacts with nuclear receptors such as ERα to promote expression their target genes. In the cytoplasm, inhibits receptor tyrosine kinase signaling through multiple mechanisms: inhibition of AKT, inhibition of SOS1-dependent activation of Ras, and suppression of ERK activation.