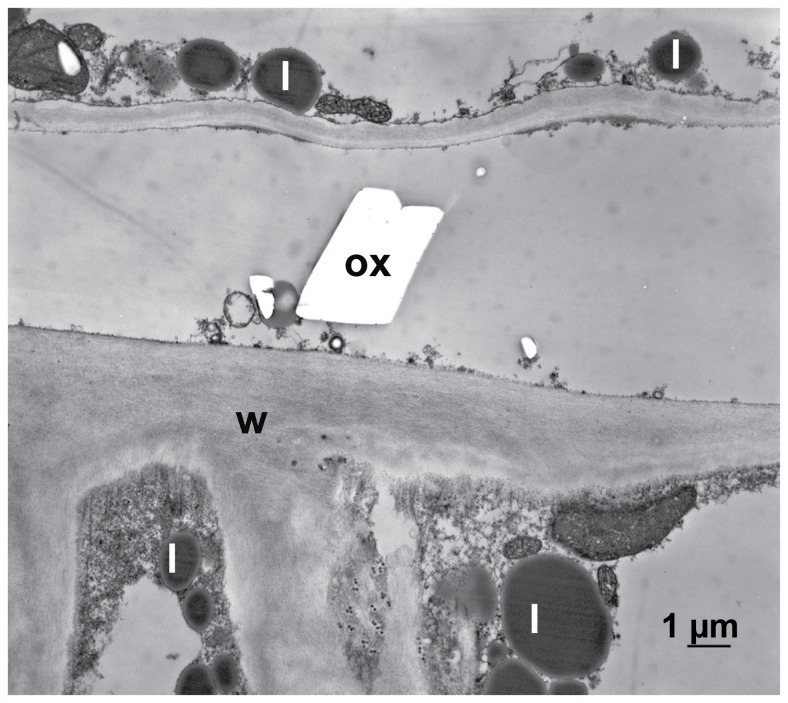
Figure 11. The Effect of oxalic acid on non-infected, inactivated host tissue.
Transmission electron micrograph of a cross section of sunflower hypocotyl. After inactivating the tissue by glutaraldehyde fixation it was treated with oxalic acid and additionally with calcium chloride to precipitated calcium oxalate: In the inactivated tissue calcium oxalate crystals (ox) appeared. The accumulation of lipid bodies (l) is indicating the beginning of decomposition of the membranous system of the cell; cell wall (w).