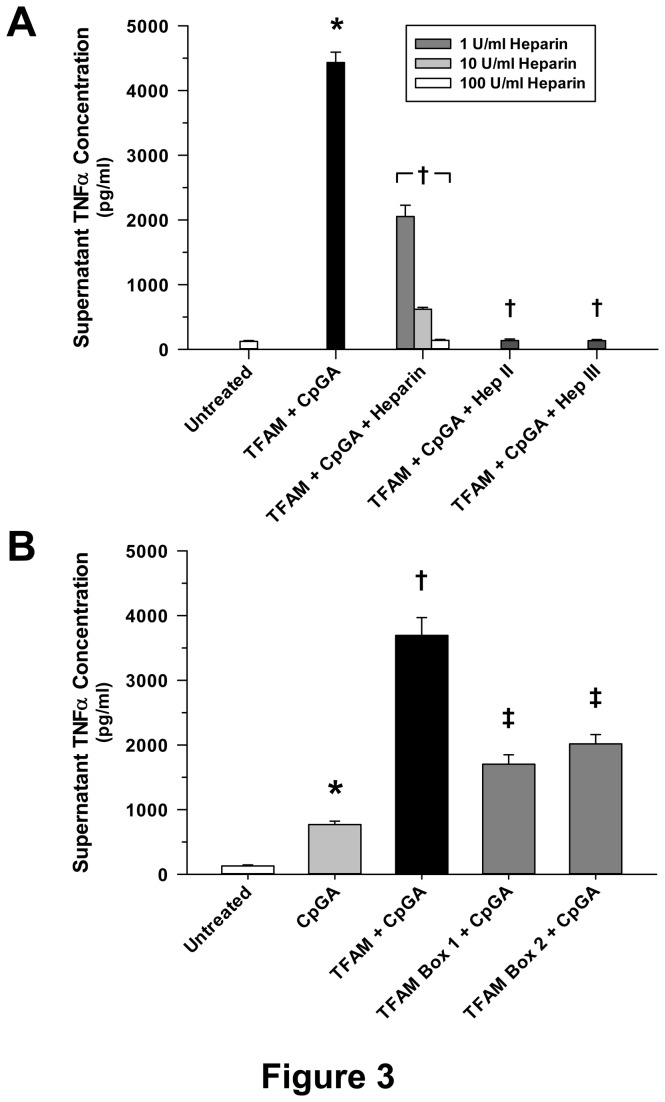
Figure 3. Enhancement by TFAM of the CpGA DNA-induced Splenocyte Proinflammatory Immune Response Results from Charge-Dependent Recognition of TFAM and Is Equipotent for Both TFAM DNA-binding Subunit Proteins, Box 1 and Box 2.
The presented data was derived from at least 5 independent experiments. (A) Pre-treatment (30 minutes) with heparin sodium (1-100 U/ml) or heparin lyase (heparinase) II or III (5 mU/ml) dramatically suppressed TFAM (5 µg/ml) + CpGA DNA (0.3 µM)-induced Flt3L-expanded splenocyte (1 × 106 cells/ml) TNFα release 24 hours post-treatment. Heparin demonstrated significant inhibition in a dose-dependent manner (*p < 0.01, compared to no treatment; † p < 0.01, relative to the TFAM + CpGA treatment group). (B) Though not as potent at augmenting CpGA DNA (0.3 µM)-induced splenocyte (1 × 106 cells/ml) TNFα release as full-length recombinant TFAM (5 µg/ml) 24 hours post-treatment, recombinant TFAM Box 1 and Box 2 (5 µg/ml) each demonstrated significant amplification of CpGA DNA-induced TNFα release (*p < 0.01, compared to no treatment; † p < 0.01, relative to CpGA DNA treatment alone, and ‡p < 0.01, compared to CpGA DNA alone and the TFAM + CpGA treatment group).