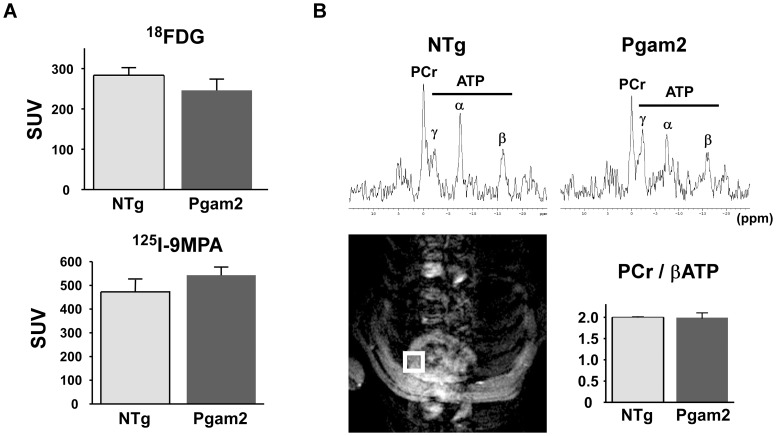
Figure 2. Myocardial substrate uptake and myocardial energy reserve were normal in Pgam2 mice.
(A) Myocardial uptake of 18F-deoxyglucose (18FDG) and 125I-15-(p-iodophenyl)-9-R,S-methylpentadecanoic acid (125I-9MPA) did not differ from that in NTg mice (n = 13 for NTg and n = 18 for Pgam2 mice). SUV: standard uptake value. SUV = tissue concentration (MBq/g)/(injected dose (MBq)/body weight (g)). (B) Cardiac energy reserve was analyzed by measuring cardiac high-energy phosphates with in situ 31P magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS). 1H magnetic resonance (MR) imaging was used to define the region of interest to measure the 31P MR spectrum of the anterior wall of the left ventricle (lower left panel). Representative in situ cardiac 31P MR spectra from NTg and Pgam2 mice are shown (upper panel). ppm: parts per million. The cardiac phosphocreatine (PCr)/βATP ratio of Pgam2 mice at rest did not differ from that of NTg mice (NTg: n = 10; Pgam2 mice: n = 9; lower right panel).