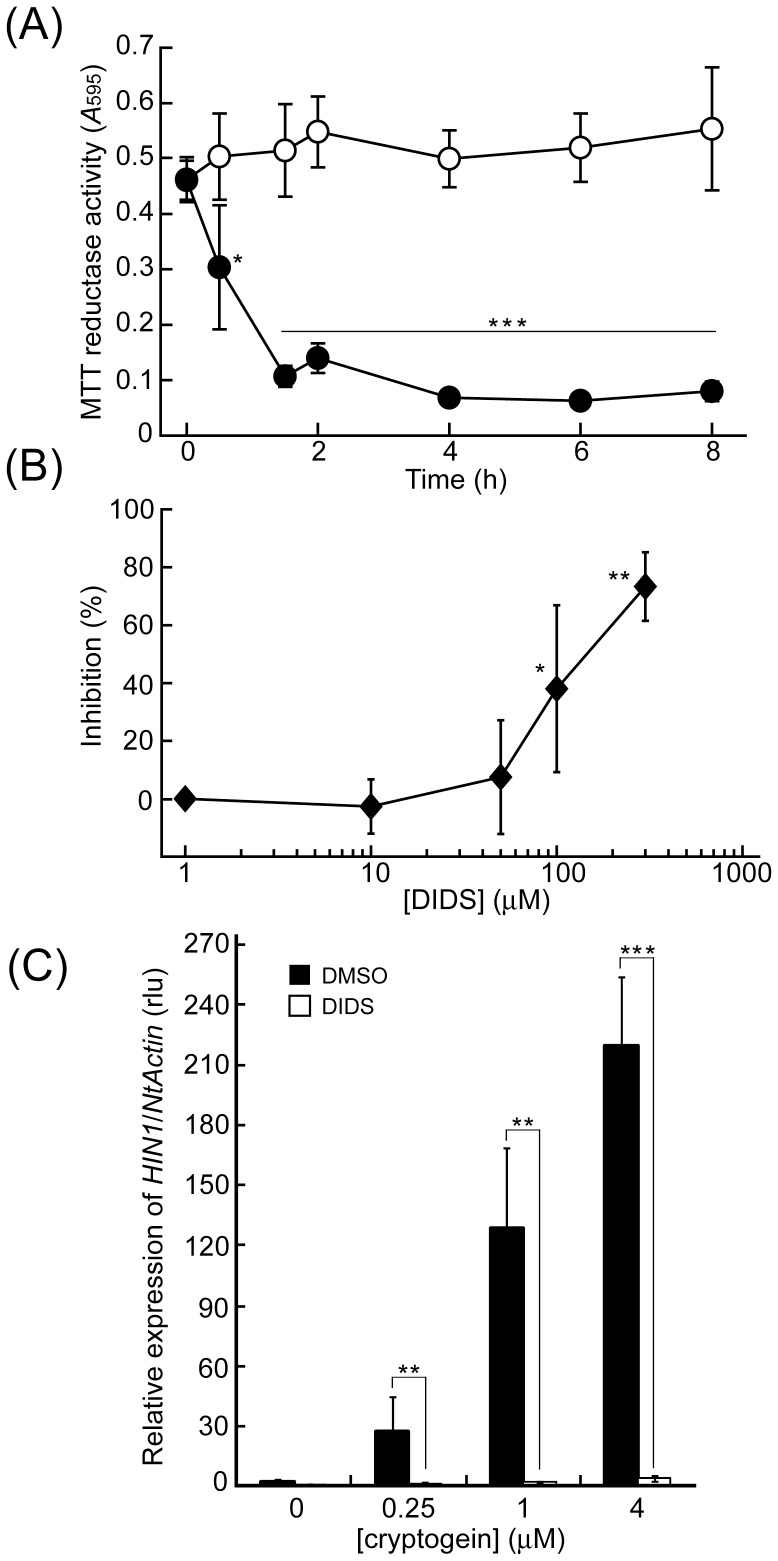
Figure 1. Effect of DIDS on cryptogein-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and expression of HIN1 in BY-2 cells.
(A) Cryptogein (1 µM)-induced reductions in MTT reductase activity. MTT reductase activity was used as a putative marker for mitochondrial dysfunction. Black circle: cryptogein treatment, white circle: water treatment as a control. *** p<0.001, significantly different from the control. (B) Inhibitory effect of DIDS on cryptogein-induced reductions in MTT reductase activity. BY-2 cells 3 h after the addition of the cryptogein elicitor (1 µM). DIDS or DMSO was added to BY-2 cells 15 min prior to the elicitor treatment. Data are the mean ± SE of three independent experiments. * p<0.05, ** p<0.005, significantly different from the control. DMSO was used as a control. (C) Effect of DIDS on cryptogein-induced HIN1 expression. Total RNA was isolated from BY-2 cells harvested 2 h after the addition of cryptogein. DIDS (white bars) or DMSO (black bars) was added to BY-2 cells 15 min prior to the elicitor treatment. The amount of each mRNA was calculated from the threshold point located in the log-linear range of RT-PCR. The relative level of each gene in control cells at time 0 was standardized as 1. Data are the mean ± SE of three independent experiments. ** p<0.005, *** p<0.001, significantly different from the control.