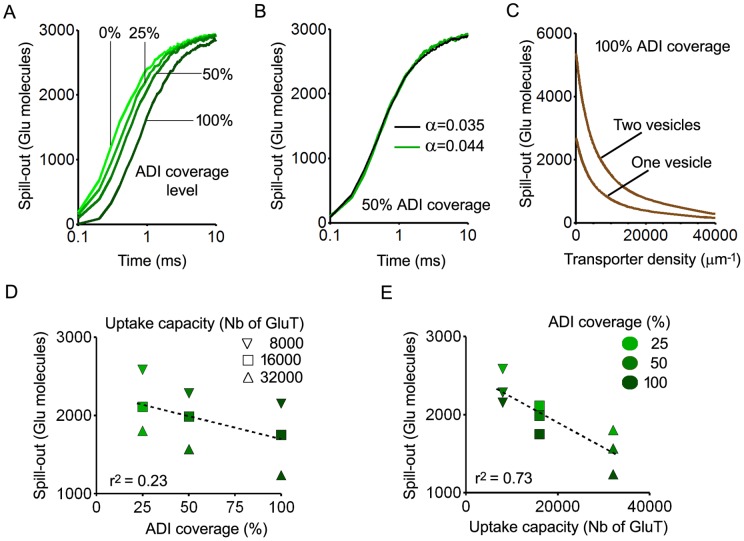
Figure 4. Effects of diffusion barriers and uptake capacity on glutamate spill-out.
A. Time course of glutamate exit from the synapse and its immediate vicinity in different conditions of ADI coverage without uptake. Increasing the proportion of ADI perimeter covered by glia delays spill-out. B. Time course of glutamate exit from the synapse and its immediate vicinity in conditions of 50% ADI coverage without uptake. The two different arrangements of glial barriers depicted in Figure 2B and C resulting in different porosity values (α = 0.044 and α = 0.035) were tested and produced nearly identical exit rates. C. Effects of uptake in conditions of full ADI coverage: final amounts of glutamate escaping the synapse as a function of transporter density. The ratio between the curves obtained for the release of one vesicle and two vesicles is a constant (0.5) indicating that no saturation occurs even with the lowest transporter densities. D and E. Regression analysis showing the respective roles of diffusion barriers and uptake in preventing spill-out.