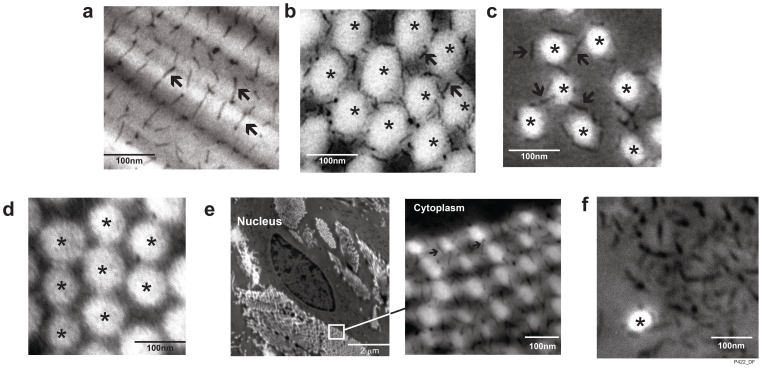
Figure 3. Ultrastructure of collagen fibril binding GAGs in human dermis.
Sulfated GAGs were stained by cupromeronic blue and visualized using electron microscopy. GAGs displayed as black thin filaments are indicated by arrows. Collagen fibrils displayed as whitish rods or circles are indicated by asterisks. (a) Longitudinal sectioned collagen fibrils. (b) Cross-sectioned collagen fibrils. (c) Cross-sectioned loosely-packed collagen fibrils. (d) Skin specimens were treated with chondroitinase to degrade GAGs prior to cupromeronic blue staining. (e) A low magnification image of a spindle-shaped cell embedded in collagen fibrils and a high magnification image showing GAG-binding collagen fibrils associated with cell. (f) Aggregated GAGs localized in spaces between collagen fibrils. Results are representative of more than 200 micrographs of dermal ECM obtained from 5 human subjects.