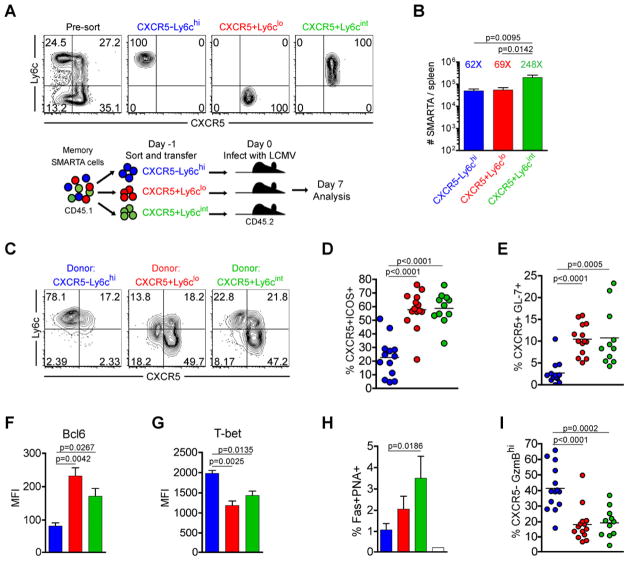
Figure 3. Th1 and Tfh memory CD4+ T cells are committed for recall of lineage-specific functions.
CD45.1 congenically marked CXCR5−Ly6chi (blue), CXCR5+Ly6clo (red), and CXCR5+Ly6cint (green) memory CD4+ subsets (between days 56 and 101 post-infection) were FACS purified to >97%. 8×103 sorted cells were adoptively transferred into naïve CD45.2 recipients, and recipient mice were then infected with LCMV Armstrong 16–20 hours later. In (C–I), the phenotype and function of transferred SMARTA cells was analyzed 7 days post-infection. A) Representative post-sort analysis of memory SMARTA subsets and cartoon of experimental setup. B) Absolute number of transferred CD4+ CD45.1+ SMARTA splenocytes 7 days following rechallenge with LCMV. The relative fold increase of each population, assuming a 10% take of transferred SMARTA cells, is shown above each bar. C) Representative CXCR5 and Ly6c analysis. D) Chart shows the percent of transferred SMARTA cells that are CXCR5+ICOS+ Tfh cells. E) The percent of SMARTA cells that are CXCR5+GL-7+ germinal center Tfh cells. F) Bcl6 MFI of SMARTA cells. G) T-bet MFI of SMARTA cells. H) Chart shows the percent of B220+ gated splenic B cells that are Fas+PNA+ germinal center B cells. Data were combined from 2 experiments. I) Chart shows the percent of transferred SMARTA cells that are CXCR5−GranzymeBhi cells. Data in B, D, E and I are combined from 4 independent experiments for a total of N=11–14 mice per group. Data in F and G were from a single experiment (N=3 per group) and were representative of 2–4 independent experiments. Statistically significant p values are shown, and were determined using a two-tailed unpaired Students t test. Error bars represent the SEM. See also Figure S3.