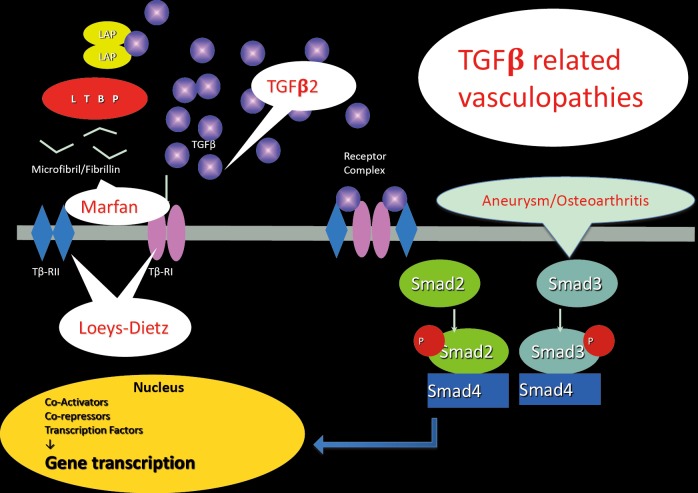
Figure 3.
The TGFβ pathway and related vasculopathies. Following its release from the Extracellular Matrix, TGFβ binds to its type II cell surface receptor (TβRII), which recruits and phosphorylates the type I receptor (TβRI). TβRI then recruits and phosphorylates SMAD2 and/or SMAD3. These P-SMADs then bind to the common SMAD (co-SMAD) SMAD4 to form a heterodimeric complex. This complex enters the cell nucleus where it acts as a transcription factor for various TGFβ-dependent genes, such as connective tissue growth factor (CTGF), plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) and multiple collagens