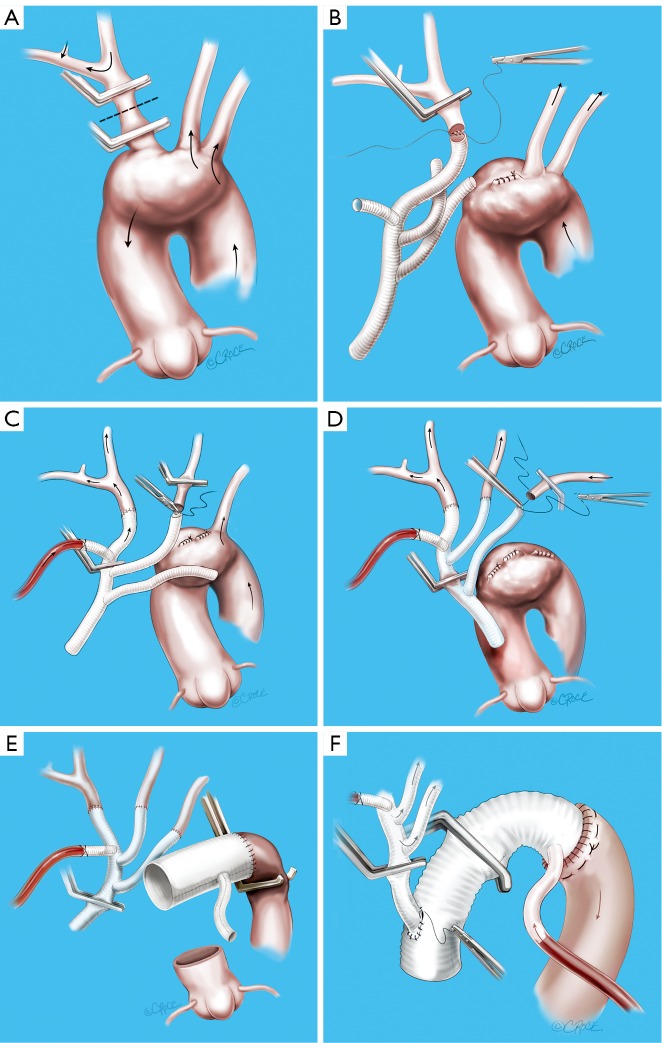
Figure 2.
Sequence of the “branch-first” aortic arch reconstruction. A. The innominate artery is clamped proximal to its bifurcation and distal to its origin from the arch. Right hemispheric cerebral perfusion is maintained through the left common carotid and subclavian arteries via collateral channels (see Figure 3); B. The innominate stump is ligated and the anastomosis to the branched graft completed; C. Antegrade right hemispheric cerebral perfusion is resumed via perfusion side arm. Left hemispheric cerebral perfusion during construction of the left common carotid anastomosis is maintained via the same collaterals (see Figure 3); D. Subclavian anastomosis is completed; E. Anastomosis of the arch graft to the distal arch. Note the clamped proximal arch allows continued perfusion of distal organs. Cardioplegia is now commenced; F. After completion of the root anastomosis, connection of the trifurcation graft to the ascending graft proceeds without interruption of cerebral perfusion