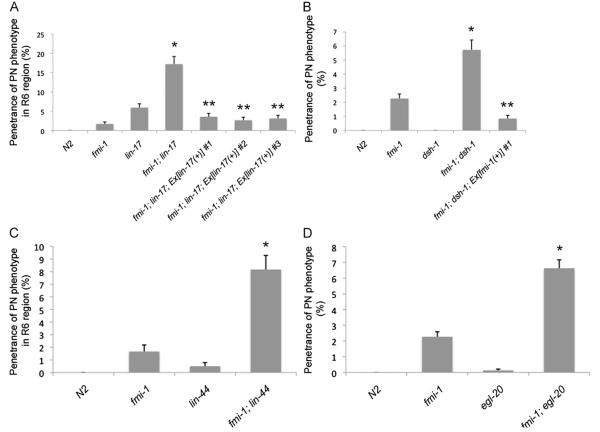
Fig. 7.
fmi-1 genetically interacts with lin-17, dsh-1, lin-44 and egl-20. (A) Quantification of the PN phenotype in region R6 in lin-17 and fmi-1 mutants and lin-17;fmi-1 double mutants using juIs76. lin-17 expression, under its endogenous promoter, rescues PN defects in lin-17;fmi-1 double mutants (last three bars). (B) Penetrance of PN defects in regions R2–R6 in dsh-1;fmi-1 double mutant animals. Defects were rescued by transgenic expression of fmi-1 in the double mutants (last bar). PNs are not present in either dsh-1 or N2 control animals. (*) indicates a significant increase in the penetrance of PN phenotype in double mutant animals compared to that of either single mutant (χ2 test, p<0.05). (**) indicates a significant decrease in the penetrance of PN phenotype in the rescue line compared to that of the double mutant animal (χ2 test, p<0.05).