Figure 1.
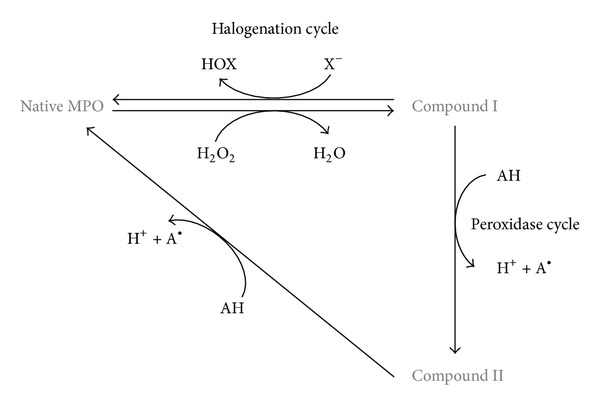
Scheme of the interconversion between different oxidized states of myeloperoxidase. The first reaction is the oxidation of native MPO to Compound I by a two-electron reaction. In the halogenation cycle, Compound I is backconverted to native MPO, and a two-electron oxidation of (pseudo-) halide generates hypo- (pseudo-) halogenous acid. In the peroxidase cycle, Compound I can oxidize an electron donor via 1-electron process transforming Compound I to Compound II and the electron donor to a radical product. Compound II can be reduced to native MPO by using 1 electron from other electron donors.
