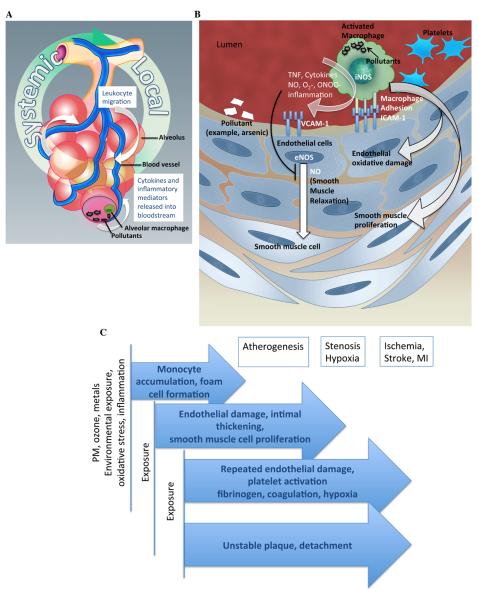
Figure 2.
Mechanism of environmental exposure mediated cardiovascular outcome. A. Air pollution induces release of cytokines and chemokines, causing inflammatory cellular recruitment and local inflammation and cyclical systemic impact through the vasculature. B. Inflammatory and oxidative stress induces atherosclerotic processes. Ingestion of particulate matter activates macrophages, induces reactive oxygen species, monocyte adhesion molecules and accumulation of monocytes on endothelial layer, foam cell transformation. Subsequently, endothelial cell dysfunction and smooth muscle cell proliferation take place. TNF, tumor necrosis factor; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; NO-, nitric oxide, O2-, superoxide; ONOO-, peroxynitrile; ICAM-1 Intercellular adhesion molecule 1; VCAM-1, Vascular cell adhesion molecule 1; eNOS, endothelial nitric oxide synthase. C. Exposure to environmental pollutants causes oxidative stress and inflammation, which triggers onset of, or exacerbates cardiovascular disease process at any stage of progression.