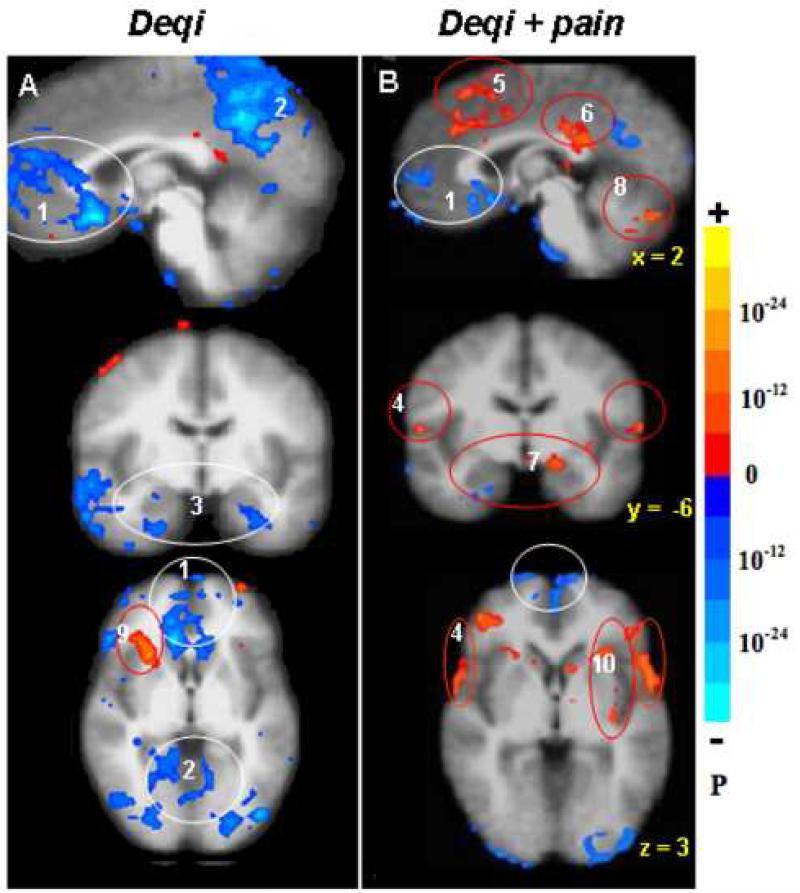
Fig. 3.
Distinct patterns of hemodynamic response between deqi (52 runs /37 subjects, A) and deqi mixed with sharp pain (52 runs/29 subjects, B) during acupuncture at right LI4, ST36 or LV3, p < 0.0001. The deactivation of the MPFC (1), MPC (2) and MTL (3) seen with deqi absent pain was attenuated in the presence of pain. With pain, activation of the sensorimotor and association cortices (4) became more prominent, and a subset of the limbic and paralimbic regions such as the midC/SMA (5), postC_BA23 (6), Amy (7), and cerebellar vermis (8) became activated. The right anterior insula (9) was markedly activated in deqi while smaller areas of anterior and posterior insula (10) were activated bilaterally in pain.