Fig. 8.
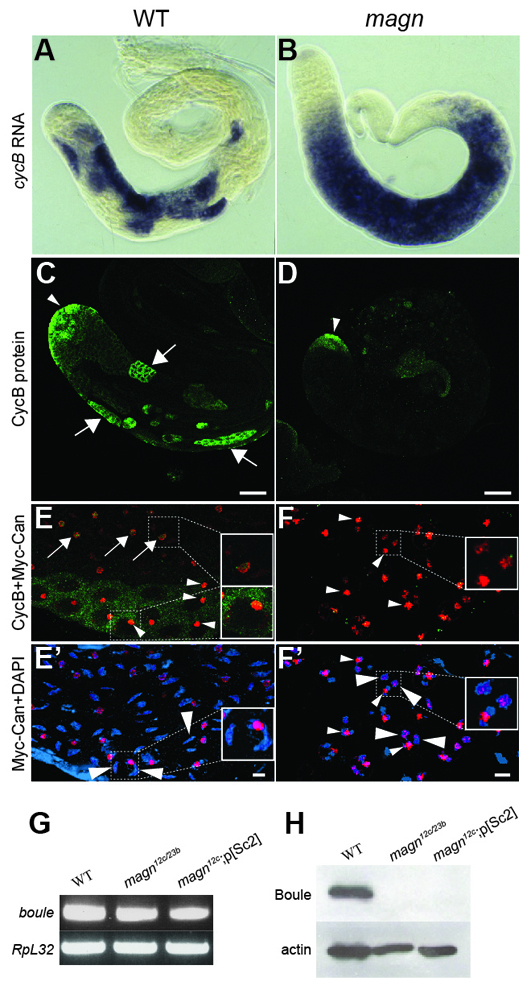
Protein, but not transcripts, of key cell cycle regulators fails to accumulate in magn spermatocytes. (A,B) In situ hybridization to (A) magn mutant and (B) wild-type testes with antisense RNA probes for CycB transcripts. (C,D) CycB protein stain in wild-type (C) and magn (D) testis. Arrowheads, CycB protein expression in spermatogonia; arrows, CycB protein expression in wild-type mature spermatocytes. (E,E′) Timing of CycB protein accumulation in wild-type mature spermatocytes. (F,F′) magn spermatocytes arrest at a stage past that of normal spermatocyte CycB accumulation. (E,F) Merge of the Myc-Can and CycB channels. Green, CycB; red, Myc-Can. (E′,F′) Merge of Myc-Can and DAPI channels. Red, Myc-Can; blue, DAPI. Large arrowheads indicate crescent-shaped autosomal bivalents in wild-type mature spermatocytes (E′) or globular arrested magn chromatin (F′). Arrows (E) indicate the less compacted circular Myc-Can nucleolar stain associated with low levels of CycB. Small arrowheads indicate the solid nucleolar Myc-Can stain associated with high levels of CycB (E) or compacted nucleolar Myc-Can stain as solid dots (F,F′). (G) RT-PCR showing mRNA expression of boule in wild-type and magn null mutant testes. RpL32 RT-PCR provided a loading control. (H) Western blot of Boule protein in wild-type and magn testes. Anti-actin provided a loading control. Thirty pairs of testes were used as starting material across the different genotypes in G and H. Scale bars: 10 μm in C,D; 4 μm in E′,F′.
