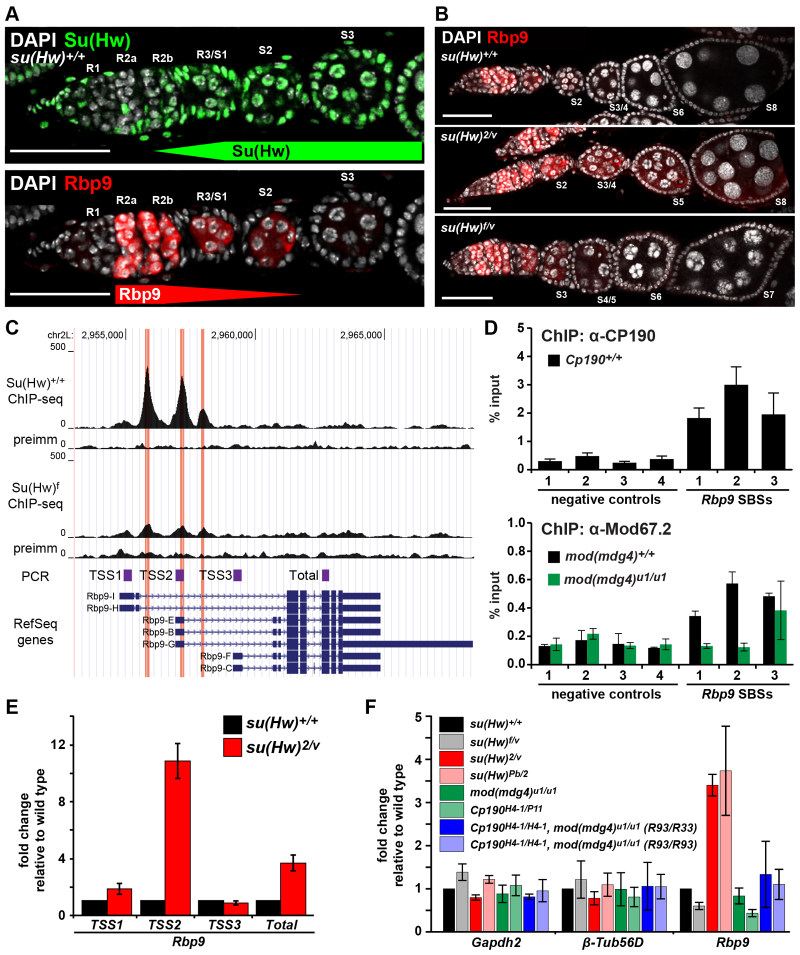
Fig. 4.
Rbp9 is repressed by Su(Hw). (A) Images of su(Hw)+/+ germarium stained for Su(Hw) (top, green), Rbp9 (bottom, red) and DAPI (white). Developmental regions (R1 to R3) of the germarium and egg chamber stages (S1 to S3) are indicated. Scale bars: 25 μm. (B) su(Hw)+/+ (top), sterile su(Hw)2/v (middle) and fertile su(Hw)f/v (bottom) ovarioles stained for Rbp9 (red) and DAPI (white). Scale bars: 25 μm. (C) UCSC genome browser view of the Rbp9 gene locus, including tracks. Top to bottom: chromosome coordinates, su(Hw)wt ChIP-Seq reads, preimmune serum IP control reads, su(Hw)f ChIP-Seq reads, preimmune serum IP control reads, fragments amplified in qPCR analyses (E), RefSeq gene annotation. (D) ChIP-qPCR analyses of ovary-bound CP190 (top) and Mod67.2 (bottom) at Rbp9 SBSs. Negative controls (1-4) were genomic regions with no SBS (Soshnev et al., 2012). ChIP from a mod(mdg4)u1 mutant background was a negative control. (E) qPCR analyses of promoter-specific Rbp9 transcripts in su(Hw)+/+ (black bars) and su(Hw)2/v (red bars) mutant background. Expression is normalized to housekeeping gene RpL32 and is shown as fold change relative to su(Hw)+/+. Error bars indicate s.d. of three biological samples. (F) qPCR analyses of gene expression changes in su(Hw), Cp190 and mod(mdg4) mutant ovaries. Expression is normalized to the housekeeping gene RpL32 and shown as a fold change relative to su(Hw)+/+. Gapdh2 and β-tubulin are negative controls. R33 and R93 indicate two independently generated recombinant chromosomes containing Cp190H4-1 and mod(mdg4)u1 mutations. Error bars indicate s.d. of two independent biological samples.