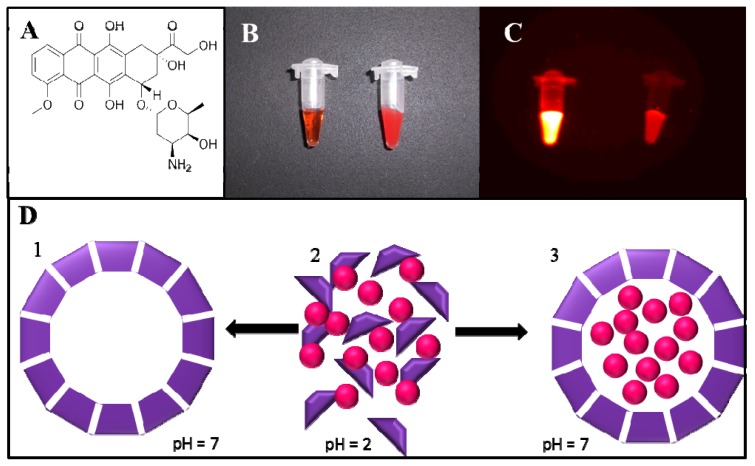
Figure 1.
(A) Chemical structure of doxorubicin (DOX); (B) Photograph of solution of DOX (left) and apoferritin encapsulated doxorubicin (APODOX) (right) in the ambient light; (C) Fluorescence photograph of solution of DOX (left) and APODOX (right)— λex = 480 nm, λem = 600 nm, exposition time 6 s, fStop 1.1, FOV 7.2; (D) Scheme of pH dependent disassembling and reassembling of apoferritin and encapsulation of DOX (1—schematic structure of assembled apoferritin at physiological conditions, 2—mixture of disassembled apoferritin units and DOX molecules at pH 2, 3) encapsulation of DOX molecules into the apoferritin cavity at increased pH and formation of APODOX).