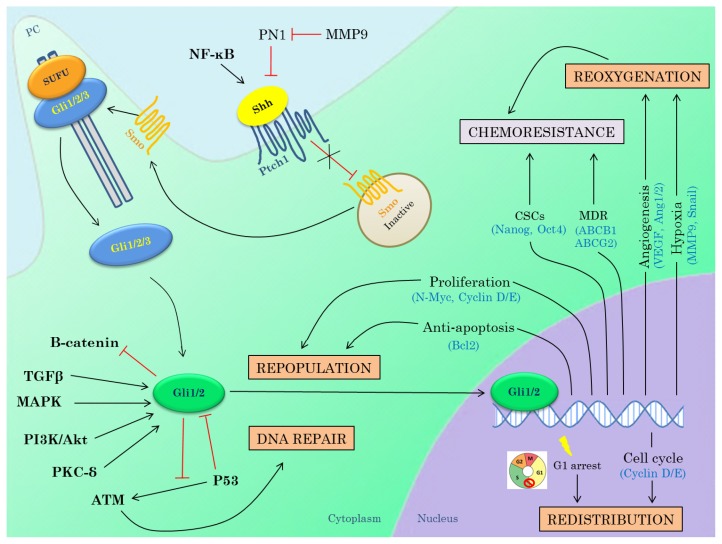
Figure 2.
Schematic overview of Hedgehog signaling and rationale for combination therapy with (chemo)radiotherapy. Upon Sonic Hedgehog (Shh) ligand binding to its receptor Patched (Ptch1) 1, the repression of Smoothened (Smo) is relieved, resulting in the movement of Smo from the intracellular vesicles to the primary cilium. Smo becomes activated and promotes the activation of the Gli proteins (Gli1/2) that enter the nucleus and promote transcription of the target genes (canonical pathway activation). The Gli transcription factors can also become activated by means of non-canonical pathway activation due to significant crosstalk with other important pathways such as the PI3K-Akt, KRAS, PKC-δ and TGFβ pathways. The Hh signaling also has important interactions with Wnt pathway and P53. The response to radiation therapy is determined by the four R’s of radiobiology: repopulation, repair of sublethal DNA damage, redistribution and reoxygenation. Hh signaling can potentially interfere with all these processes and targeting Hh signaling could therefore increase radiosensitivity of tumor cells. Moreover, inhibition of Hh signaling could also improve the response to chemotherapy by targeting multidrug resistance and cancer stems cells in addition to its effects on tumor vasculature. Abbreviations: PC, primary cilia; MDR, multidrug resistance; CSCs, cancer stem cells.