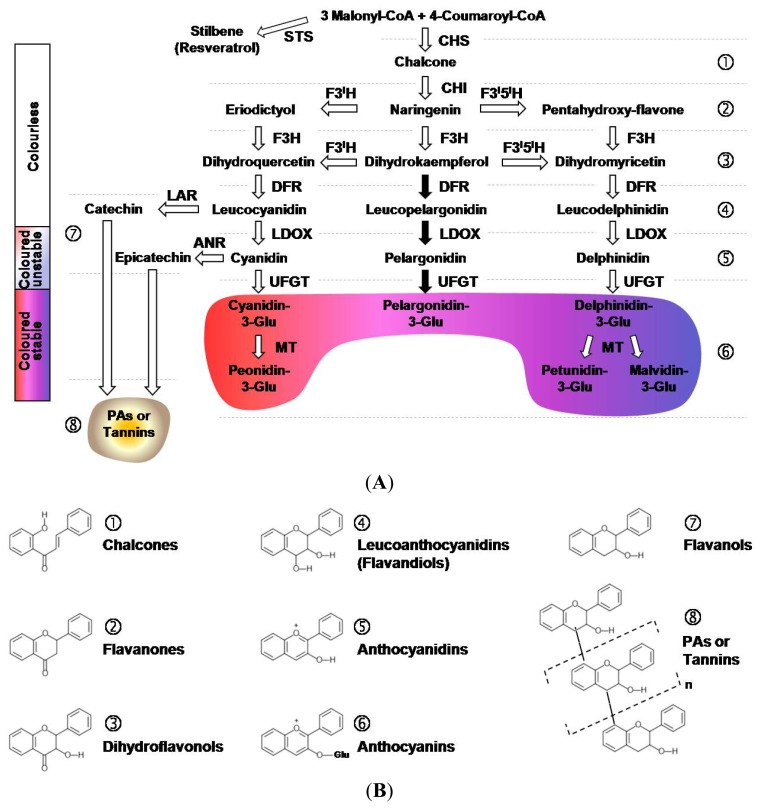
Figure 1.
(A) Scheme of the flavonoid biosynthetic pathway in plant cells. Anthocyanins are synthesized by a multienzyme complex loosely associated to the endoplasmic reticulum (CHS, chalcone synthase; CHI, chalcone isomerase; F3H, flavanone 3-hydroxylase; F3′H, flavonoid 3′-hydroxylase; F3′5′H, flavonoid 3′,5′-hydroxylase; DFR, dihydroflavonol reductase; LDOX, leucoanthocyanidin oxidase; UFGT, UDP-glucose flavonoid 3-O-glucosyl transferase; MT, methyltransferase). Proanthocyanidins (PAs) synthesis branches off the anthocyanin pathway (LAR, leucoanthocyanidin reductase; ANR, anthocyanidin reductase; STS, stilbene synthase); the black arrows refer to biosynthetic steps missing in grapevine. Numbers next to the flavonoid groups are related to the chemical structures shown in (B). (B) Chemical structures of the major flavonoid groups.