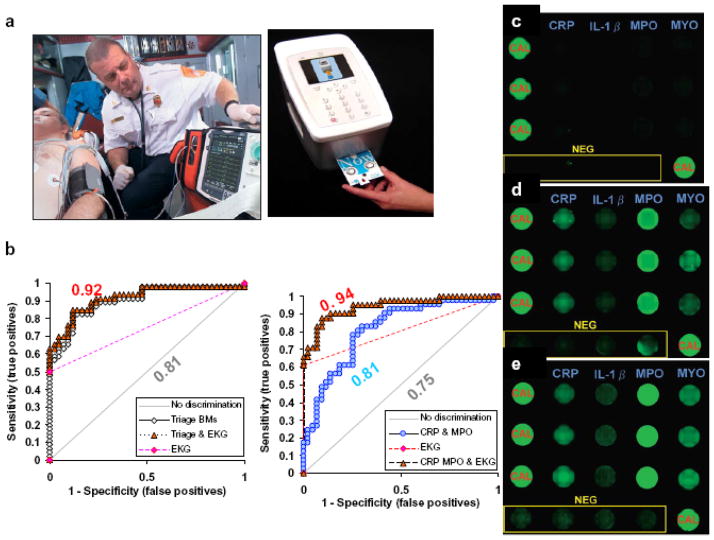
Figure 2. Saliva AMI testing in ambulance.
(a) 12 lead EKG used by paramedics to transmit initial findings to emergency room physicians (left). The portable saliva-based diagnostics NBC platform can complement EKG for the identification of AMI cases. (b) Logistic regression and ROC analysis using serum and salivary biomarkers in conjunction with EKG exhibited improvement of diagnosis of AMI. The EKG and AMI biomarkers of 42 healthy controls, 46 AMI (23 NSTEMI and 23 STEMI) are measured and compared. In serum, the ROC curve was improved from 0.81 to 0.92 in triage biomarkers (cTnI, myoglobin and CK-MB) were used as diagnostic indexes (left). However, the combined use of salivary CRP and MPO in conjunction with EKG (right), produced an excellent ROC 0.94 (i.e., >90% specificity and sensitivity of AMI diagnosis). (c) Multiplex lab-on-a-chip (LOC) for AMI biomarker antigens screening. Examples of fluorescence micrographs of a LOC multiplex assay for CRP, IL-1_, MYO and MPO are shown for non-AMI control, (d) NSTEMI and (e) STEMI patients. NEG, negative; CAL, calibrator (Modified from Floriano et al. Clin Chem, 2009 40).