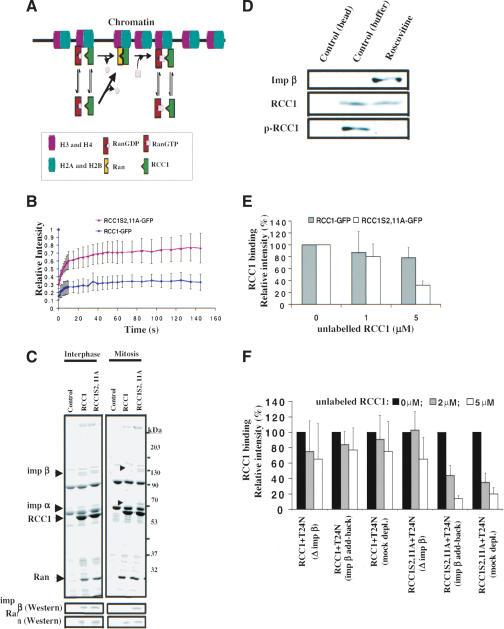
Figure 6.
Importin α and β negatively regulate RanGTP production in mitosis. (A) The chromosome-coupled exchange mechanism. Core histones, Ran, and RCC1 are shown. As individual proteins, Ran and RCC1 weakly interact with chromatin via histones H3/H4 and histones H2A/H2B, respectively. However, formation of the binary complex of RCC1–Ran during nucleotide exchange allows the binary complex to bind to chromatin stably and irreversibly. Nucleotide exchange on Ran dissociates the binary complex into RanGTP and RCC1, thereby coupling RanGTP production to mitotic chromosomes. (B) FRAP analysis of RCC1 mobility in vivo. RanT24N was injected into the mitotic cytosol of cells expressing RCC1-GFP or RCC1S2,11-GFP followed by FRAP of RCC1 on mitotic chromosomes. RCC1-GFP, but not RCC1S2,11A-GFP, was immobilized on mitotic chromosomes. Error bars show S.D. from at least five independent experiments. (C) Phosphorylation of RCC1 in mitosis prevents its interaction with importin α and β. Purified 6His-RCC1 or 6His-RCC1S2,11A was incubated with interphase or mitotic egg extracts. Both forms of RCC1 bound to similar amounts of Ran. The 95-kD and 50-kD proteins that specifically interacted with RCC1S2,11A in mitosis (see arrowheads) were identified by microsequencing as importin α and β, respectively. Western blotting further confirmed the identity of importin β and Ran. (D) Unphosphorylated RCC1 binds to importin β in mitotic HeLa cells. Roscovitine or control buffer was used to inhibit Cdc2 kinase activity in the mitotic HeLa cells. Beads alone or beads bound to 6His-RanT24N were used to pull down RCC1 from the HeLa cell lysates. Western blotting revealed that roscovitine blocked RCC1 phosphorylation (as revealed by phosphospecific antibody, p-RCC1), which allowed RCC1 to bind importin β. (E) Competition experiments. The binding of RCC1-GFP or RCC1S2,11A-GFP to mitotic chromosomes in the presence of RanT24N was completed using an increasing concentration of unlabeled 6His-RCC1 or 6His-RCC1S2,11A, respectively. Histograms show the relative fluorescence intensity of GFP-labeled RCC1 on mitotic chromosomes under different conditions. RCC1S2,11A-GFP exhibits a weaker binding than RCC1-GFP. (F) Importin β inhibits the binding of RCC1S2,11A to chromosomes. Egg extracts depleted of importin β with or without add-back of importin β along with mock-depletion controls were used to assemble mitotic chromosomes in the presence of RanT24N. The binding of RCC1-GFP or RCC1S2,11A-GFP to the chromatin in the presence of unlabeled RCC1 competitors is quantified. Depletion of importin β allows binding of RCC1S2,11A-GFP to chromatin as strongly as RCC1-GFP.