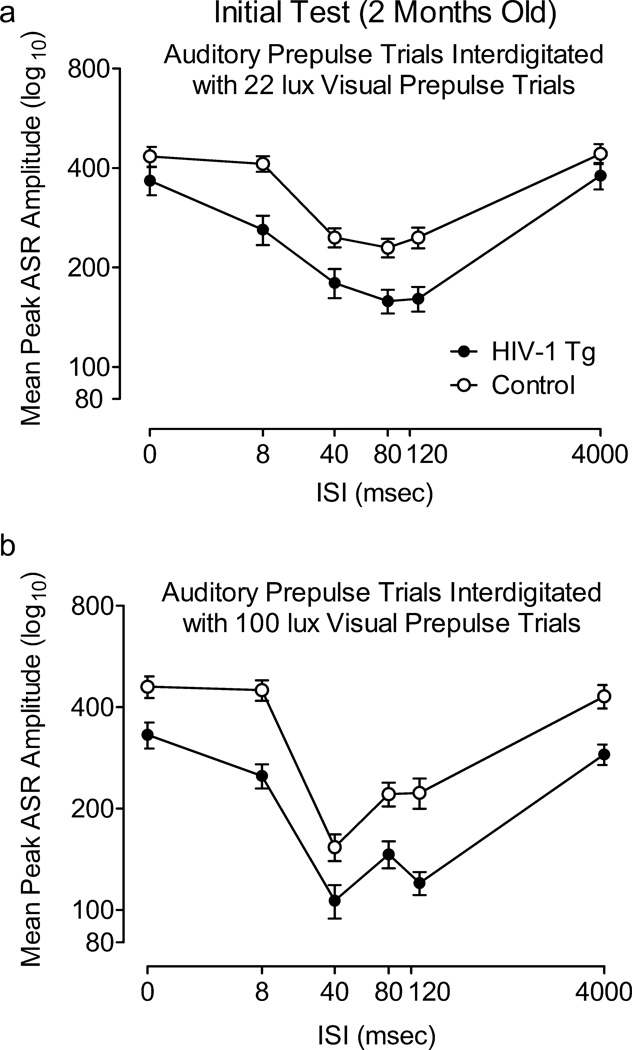
Fig. 3.
Prepulse inhibition (PPI) with an auditory prepulse during sessions interdigitated with 22 lux (A) and 100 lux (B) visual prepulse trials conducted at 2 months of age. A significant condition × interstimulus interval (ISI) interaction was detected, indicating that the HIV-1 Tg rats were less sensitive to the manipulation of ISI, as illustrated by their flatter ISI functions. Both groups’ ISI functions changed in a similar manner with the increased visual prepulse intensity; i.e., there was a leftward shift in peak inhibition to the 40 msec ISI, and the ISI functions sharpened. Percent PPI at point of peak inhibition: 1 light: HIV-Tg, 30.0%±5.5, Control, 15.2%±7.8; 2 lights: HIV-1 Tg, 46.3%±5.2; Control, 44.0%±4.5.