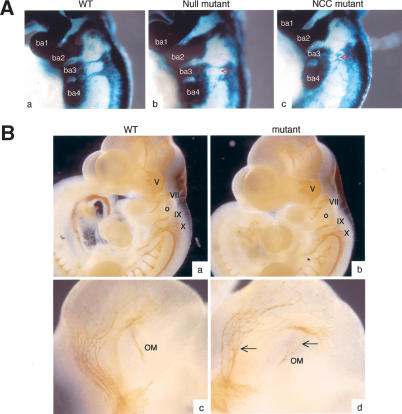
Figure 5.
Loss of ephrin-B1 induces NCC migration defects. (A) Whole-mount X-gal staining of E9.5 wild-type (panel a), ephrin-B1null (panel b), or ephrin-B1NCC (panel c). Mutant NCC exhibit a wandering behavior in ephrin-B1null (panel b) and ephrin-B1NCC embryos (panel c), as compared with wild-type (panel a). Mutant cells invade territories that are normally devoid of crest cells (red arrows). (B) Whole-mount immunohistochemistry staining of E10.5 wild-type (panels a,c) and ephrin-B1null (panels b,d) embryos using a neurofilament antibody. Cranial ganglia V-X appear normal in the mutant embryos, but branching (asterisk) and fasciculation (arrow) defects can be observed. (ba) Branchial arches; (o) otic vesicle; (OM) occulomotor nerve.