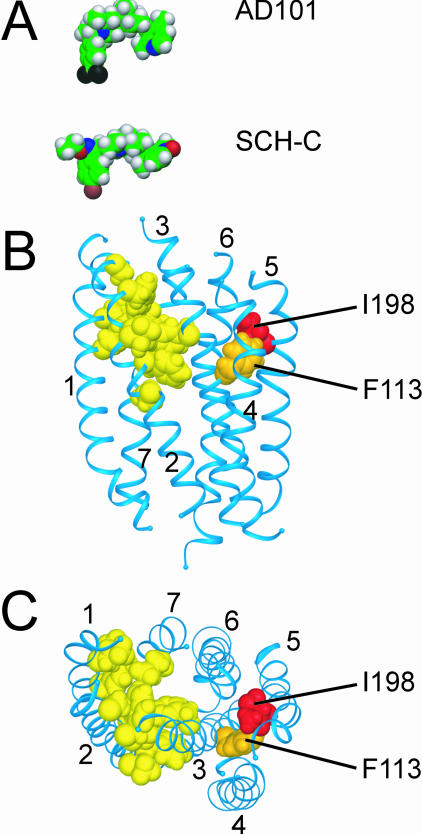
FIG. 4.
Structural model of the TM domain of CCR5 with energy-minimized structures of AD101 and SCH-C. (A) Energy-minimized structures of AD101 and SCH-C were calculated by using the PM3 semiempirical method of the HyperChem software (Hypercube, Inc.) (63) and are depicted in space-filling representation. Atoms are color-coded: carbon, green; oxygen, red; nitrogen, blue; hydrogen, grey; bromine, brown; fluorine, black. (B) Structural model of the TM domain of CCR5 viewed from within the plane of the membrane. The extracellular surface is oriented toward the top of the figure; the cytoplasmic surface is oriented toward the bottom. The seven α-helical TM segments are depicted as blue ribbons. Amino acid side chains of residues involved in the interaction of CCR5 with AD101 and/or SCH-C are shown in space-filling representation. Red, residue I198; orange, F113; yellow, L33, Y37, D76, F79, W86, V83, A90, Y108, E283, and G286. (C) View of the CCR5 model from the extracellular side of the membrane after rotation of the model by approximately 90° out of the paper plane from the orientation shown in panel B. Labeling and color-coding are the same as for panel B. The CCR5 model is based on homology with rhodopsin by using the crystal structure of bovine rhodopsin as a template (63). Models in all panels are shown at the same scale.