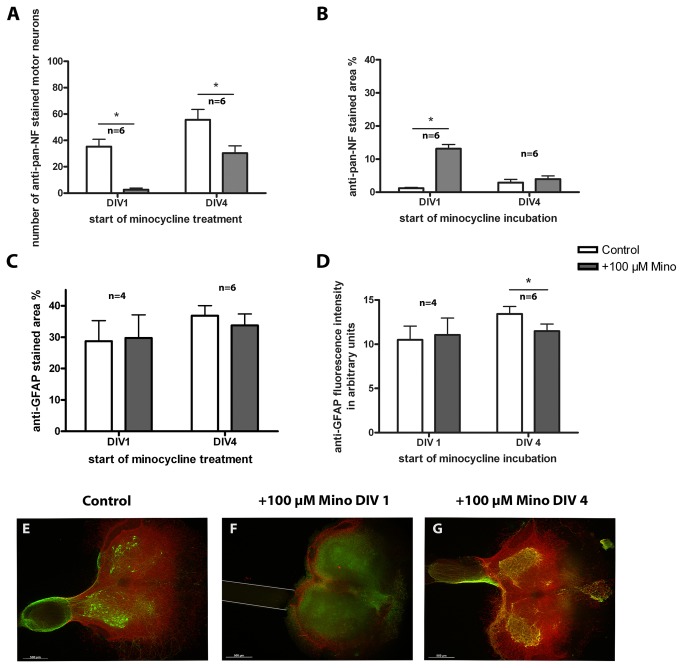
Figure 7. Treatment of organotypic spinal cord co-cultures with 100 µM minocycline.
Comparison of control and +Mino organotypic spinal cord co-cultures cultured for 7 days. +Mino co-cultures were incubated starting at DIV 1 or DIV 4. (A) number of motor neurons. Minocycline reduced the number of motor neurons compared to the control. (B) anti-pan-NF percentage stained area. Minocycline incubation from DIV 1 onwards resulted in an increased stained neurofilament respectively neurites area compared to the control. Incubation from DIV 4 onwards did not affect the percentage stained area. (C) anti-GFAP percentage stained area. (D) anti-GFAP fluorescence intensity. Neither astroglial percentage stained area nor fluorescence intensity was altered by minocycline. To compare controls and +Mino a paired Student’s t-test was used. Number of samples was n=6 except DIV 1 DAPI stained area with n=4 (1 animal = mean of up to 3 replicates). All values are means ± SD. Significant differences are marked with * and demonstrate p<0.05. (E–G) Fluorescence images of organotypic spinal cord co-cultures. A control culture is illustrated in (E) showing anti-pan-NF (green) stained motor neurons which grew neurites into the reconstructed ventral root. Astroglia (anti-GFAP, red) formed a glia cover on the surface of the slice. (F) demonstrates a co-culture incubated with minocycline from DIV 1 onwards lacking motor neurons and fiber outgrowth to the peripheral nerve graft that was opposed to the ventral side of the spinal cord slice (marked with grey lines). Astroglia staining shows peripheral distribution. (G) shows a co-culture treated from DIV 4 onwards. This culture shows several motor neurons, reconstruction of the ventral root and a glia cover. Bars = 500 µm.