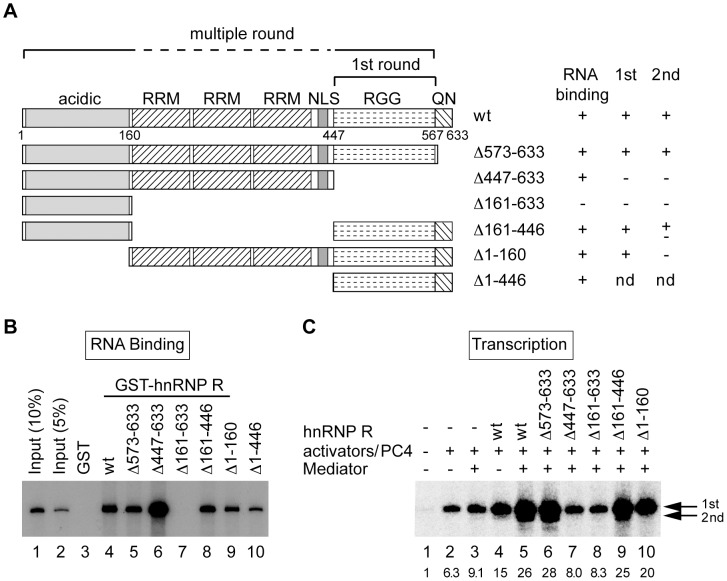
Figure 6. Functional domains of hnRNP R required for facilitating initiation and reinitiation.
(A) Schematic diagram of the domain structure of hnRNP R and its deletion mutants are shown. hnRNP R is comprised of the acidic domain (acidic), three RNA recognition motifs (RRMs), a nuclear localization signal (NLS), arginine-glycine-glycine-rich domain (RGG) and the glutamine-asparagine-rich domain (QN). The results of RNA binding assays (shown in B) and in vitro transcription (shown in C) for the mutants are summarized on the right. An in vitro transcription assay for Δ1-446 was not done (nd) because the mutant was insoluble unless expressed as a GST-fusion protein. The domains required for initiation (1st round) and reinitiation (multiple round) are indicated above the diagram. (B) Binding of the hnRNP R to the RNA derived from the 390-nt G-free cassette was assayed using immobilized GST (lane 3), GST-hnRNP R (lane 4), or GST-hnRNP R mutants (lanes 5–10). The bound RNA was analyzed by electrophoresis and autoradiography, and lanes 1 and 2 contained 10% and 5% of the input RNA. (C) In vitro transcription was preformed using the purified FLAG-tagged hnRNP R mutants. pfMC2AT harboring the 390-nt G-free cassette was used as a template. The positions of the first-round and second-round transcripts are indicated by arrows on the right, and the relative levels of the first-round transcript are indicated below each lane.