Figure 3. Diverse chimeric riboswitches are functional.
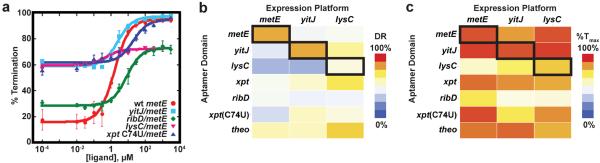
(a) Comparison of the in vitro transcription data quantified, plotted and fit to a two-state transition as a function of ligand concentration. The B. subtilis metE riboswitch wild type (wt) in red circles, compared to chimeras containing a different SAM-binding aptamer (yitJ/metE, cyan), a flavin mononucleotide (FMN) aptamer (ribD/metE, green), a lysine binding aptamer (lysC/metE, pink), and the xpt(C74U) aptamer (blue). The values for T50, dynamic range (DR) and % termination at saturating ligand concentrations are given in Table 1. In all experiments the riboswitch was titrated with the cognate effector of the aptamer. Error bars represent the standard deviation of at least three independent experiments. (b) Heat map of the dynamic range for eighteen chimeric riboswitches. The heavy box denotes the wild type metE, yitJ and lysC riboswitches. (c) Heat map for the maximal termination at high effector concentration for the riboswitches of this study.
