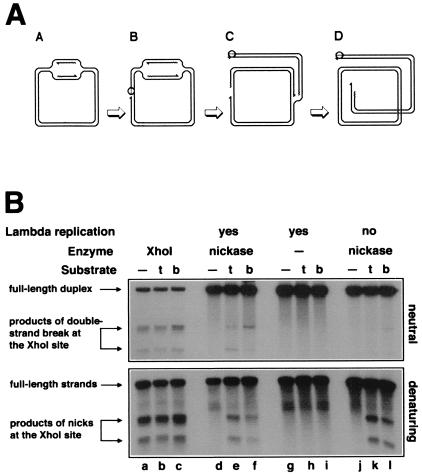
Figure 4.
Replication-induced double-strand breaks at persistent nicks at the natural XhoI-site. (A) Replication of a circular λ chromosome containing a nick is predicted to generate one circular chromosome and one linear chromosome with a double-strand break at the nick. Nicking enzyme is shown as an open circle attached to the 5′-end of the nick; 3′-ends are indicated by half-arrows, and RNA primers are marked by wavy lines. (A) Initiation of theta replication in the circular λ chromosome. (B) The nicking site is nicked while the theta replication continues. (C) The first replication fork runs into the nick and collapses, switching the chromosome to sigma replication. (D) The second replication fork reaches the single-strand interruption, resulting in a double-strand break in one of the replicated chromosomes. (B) Phages MMS2660, λAK2, or λAK3, indicated in the entry “substrate” as “—”, “t,” or “b,” respectively, were infected at moi = 10 into the strains described below; the cells were incubated at 37°C for 40 min (unless indicated otherwise), and the phage DNA was extracted and analyzed by restriction digestion with EcoRI and blot hybridization with probe 1 under both neutral (Upper gel) and denaturing (Lower gel) conditions. Molecular weight markers for double-strand break at the XhoI site were generated in vivo (lanes a–c). The strains and conditions are as follows: lanes a–c, recB268 pK107, incubated for 10 min at 37°C; lanes d–f, Δrep∷kan recD1011 pK125 + IPTG; lanes g–i, Δrep∷kan recD1011 pK125, no induction; lanes j–l, Su− Δrep∷cam recC1010 pK125 + IPTG. To compensate for the smaller amount of λ DNA because of the inhibition of λ replication, 25 times more total DNA has been loaded in the case of Su− samples (lanes j–l).