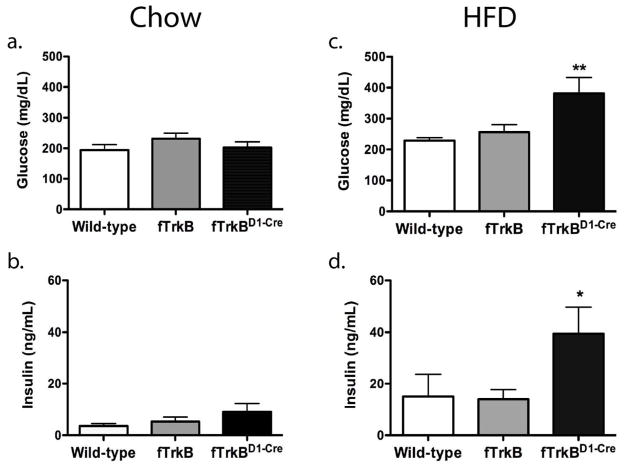
Figure 2. Loss of Trk B signaling in dopamine-1 receptor neurons exacerbates high fat diet-induced insulin resistance.
One-Way ANOVAs indicated no significant differences between groups for plasma glucose or insulin after consuming regular chow (2a and 2b, respectively). A One-way ANOVA reported fTrkBD1-Cre mice having significantly higher plasma glucose after consuming high-fat diet than both the fTrkB mice and the wild-type mice (2c; F(2,22)=5.90, p=0.0089) and also significantly different plasma insulin after consuming high-fat diet (2d; F(2,25)=3.539, p=0.04).