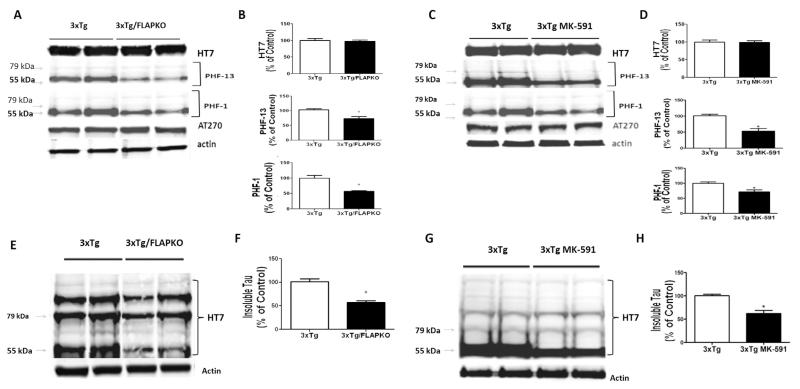
Figure 3.
5-lipoxygenase activating protein (FLAP) modulates tau phosphorylation and metabolism in the brains of triple transgenic (3×Tg) mice. (A) Representative Western blot analyses for total tau (HT-7) and phosphorylated tau at residues T181(AT270), S396(PHF-13), and S396/S404(PHF-1) in homogenates of brain cortices from 3×Tg mice and 3×Tg mice genetically deficient for FLAP (3×Tg-FLAPKO) at 14 months of age. (B) Densitometric analyses of the immunoreactivities to the antibodies shown in panel A (*p < .01). (C) Representative Western blot analyses for total tau (HT-7) and phosphorylated tau at residues T181(AT270), S396(PHF-13), and S396/S404(PHF-1) in homogenates of brain cortices from 3×Tg mice and 3×Tg mice treated with MK-591. (D) Densitometric analyses of the immunoreactivities to the antibodies shown in panel A (*p < .001). (E) Representative Western blot analyses for insoluble tau in brain homogenates from cortices of 3×Tg and 3×Tg-FLAPKO mice at 14 months of age. (F) Densitometric analyses of the immunoreactivity to the antibody shown in panel E (*p < .001). (G) Representative Western blot analyses for insoluble tau in brain homogenates from cortices of 3×Tg and 3×Tg mice treated with MK-591. (H) Densitometric analyses of the immunoreactivity to the antibody shown in G (*p < .001).