Table 2. Statistically significant differences in the nodal parameters of the anatomical networks between the conventional DTI (C-DTI) and FLAIR-DTI (F-DTI) datasets.
| Regions Classification | t-value (C-DTI) - (F-DTI) | p-value | |||
| Ki | Ei-glob | Ki | Ei-glob | ||
| FFG.R | Association | −3.310 | −3.698 | 0.004* | 0.001** |
| HIP.R | Subcortical | −3.909 | −3.987 | 8.857e-4** | 7.247e-4** |
| HES.R | Primary | – | −2.906 | – | 0.009* |
| IFGoperc.L | Association | – | −3.536 | – | 0.002** |
| IFGtriang.L | Association | – | −3.311 | – | 0.004* |
| ITG.R | Association | – | −2.940 | – | 0.008* |
| LING.R | Association | – | −3.334 | – | 0.003 |
| PHG.R | Paralimbic | −4.919 | −4.385 | 8.284e-5** | 2.863e-4** |
| PoCG.L | Primary | −2.972 | – | 0.008* | – |
| ROL.L | Association | −3.042 | −3.142 | 0.006* | 0.005* |
Note: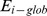 and
and 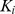 represent nodal global efficiency and degree, respectively. Bold, italic text indicates that these common brain regions showed statistically significant differences in the anatomical networks corresponding to the two types of DTI datasets with respect to both the parameters,
represent nodal global efficiency and degree, respectively. Bold, italic text indicates that these common brain regions showed statistically significant differences in the anatomical networks corresponding to the two types of DTI datasets with respect to both the parameters, 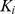 and
and 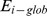 . A negative t-value indicates that the value of the nodal parameter corresponding to the FLAIR-DTI datasets is higher than that of the conventional DTI dataset. The symbol “–” shows that these regions were not statistically significantly different with respect to
. A negative t-value indicates that the value of the nodal parameter corresponding to the FLAIR-DTI datasets is higher than that of the conventional DTI dataset. The symbol “–” shows that these regions were not statistically significantly different with respect to 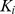 or
or 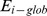 .
.
p<0.01 (uncorrected),
p<0.05 (FDR corrected).
