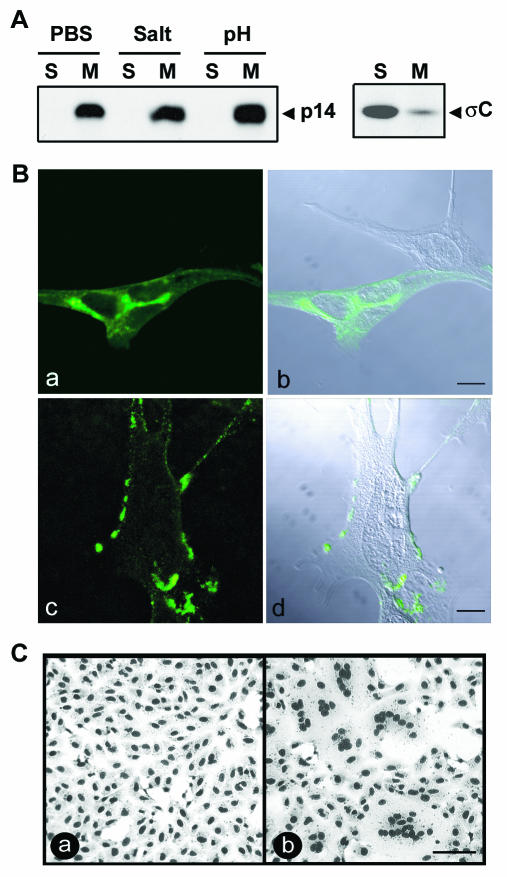
FIG. 3.
p14 is a surface-localized integral membrane protein. (A) The membrane pellet from radiolabeled, p14-transfected QM5 cells was isolated by centrifugation. Membrane pellets were treated with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) or stripped with either high salt or high pH to remove peripheral proteins, and the integral membrane (M) or soluble (S) fractions were isolated by centrifugation. The presence of p14 in each fraction was detected by immunoprecipitation using an anti-p14 polyclonal antiserum. A similar analysis was performed with transfected cells expressing the soluble ARV σC protein (right panel) as a control for the membrane isolation protocol. (B) p14-transfected QM5 cells were immunostained at 6 h posttransfection with an anti-p14 polyclonal antibody, and antibody distribution was detected by immunofluorescence microscopy using a FITC-conjugated secondary antibody (a and c). The corresponding differential interference microscopy (DIC) images overlaid with the fluorescent images are also shown (b and d). Cells were permeabilized by methanol fixation prior to antibody staining to reveal intracellular p14 distribution (a and b) or were stained live to reveal cell surface expression of p14 (c and d). Scale bar = 10 μm. (C) Transfected Vero cells expressing p14 were treated with anti-p14 polyclonal antiserum (a) or normal rabbit serum (b). Cells were fixed with methanol at 14 h posttransfection and Giemsa stained to reveal the inhibition of syncytium formation by the anti-p14 antiserum. Scale bar = 100 μm.