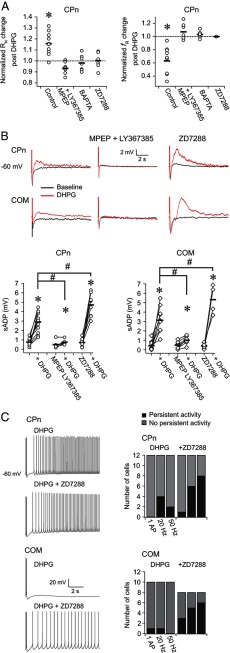
Figure 4.
Mechanisms contributing to short- and long-term changes in L5 neurons after DHPG application. A, There were no changes in the subthreshold membrane properties of CPn neurons in response to 20 μm DHPG in the continued presence of the mGluR5 antagonist MPEP (40 μm) and the mGluR1 antagonist LY367385 (50 μm). There were also no changes when 20 mm BAPTA or 10 μm ZD7288 was included in the recording pipette. Similar results were obtained for sag and rebound (data not shown). *p < 0.001 (paired t test). B, MPEP (40 μm) and LY367385 (50 μm) largely prevented DHPG-mediated changes in the sADP in both cell types. Inclusion of ZD7288 (10 μm) in the recording pipette produced a larger sADP than control conditions. Data are from bursts of 5 action potentials at 50 Hz. Similar data were obtained for a single or burst of action potentials at 20 Hz (data not shown). *p < 0.05 (paired t test). #p < 0.05 (independent sample t test, Bonferroni corrected). In 9 of 12 CPn neurons and 4 of 8 COM neurons, the sADP could be measured after DHPG application in the ZD7288 condition. The remaining neurons fired persistently on each trial of the sADP test. C, Including 10 μm ZD7288 in the recording pipette also increased the propensity of both cell types to fire persistently in the presence of DHPG.