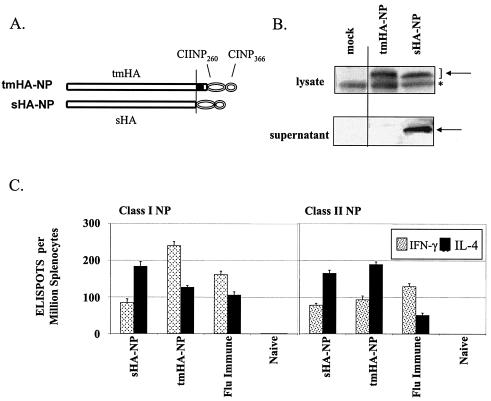
FIG. 1.
DNA vaccines, expression, and immune responses. (A) DNA expression vectors encoding transmembrane and secreted forms of HA coupled with the H-2Db-restricted class I NP366-374 (CINP366)- and class II NP260-283 (CIINP260)-designated tmHA-NP and sHA-NP, respectively (12). (B) Western blot of the expressed proteins. The Western blot used polyclonal mouse sera that recognized influenza A (H1N1). The specific bands are denoted by the arrows, and a nonspecific band is represented by an asterisk. (C) Ex vivo ELISPOT analyses of splenocytes harvested 4 weeks after gene gun vaccination of C57BL/6 mice with 2 μg of DNA at 0 and 4 weeks (for a review of the methods, see reference 12). Responding cells were stimulated with peptides representing amino acids 366 to 374 (Class I) and amino acids 260 to 283 (Class II) of NP. The immunizing DNA and the lymphokine tested for in the assays are indicated below the bars. Bars indicate the average response ± the standard deviation for groups of five mice.