Fig. 1.
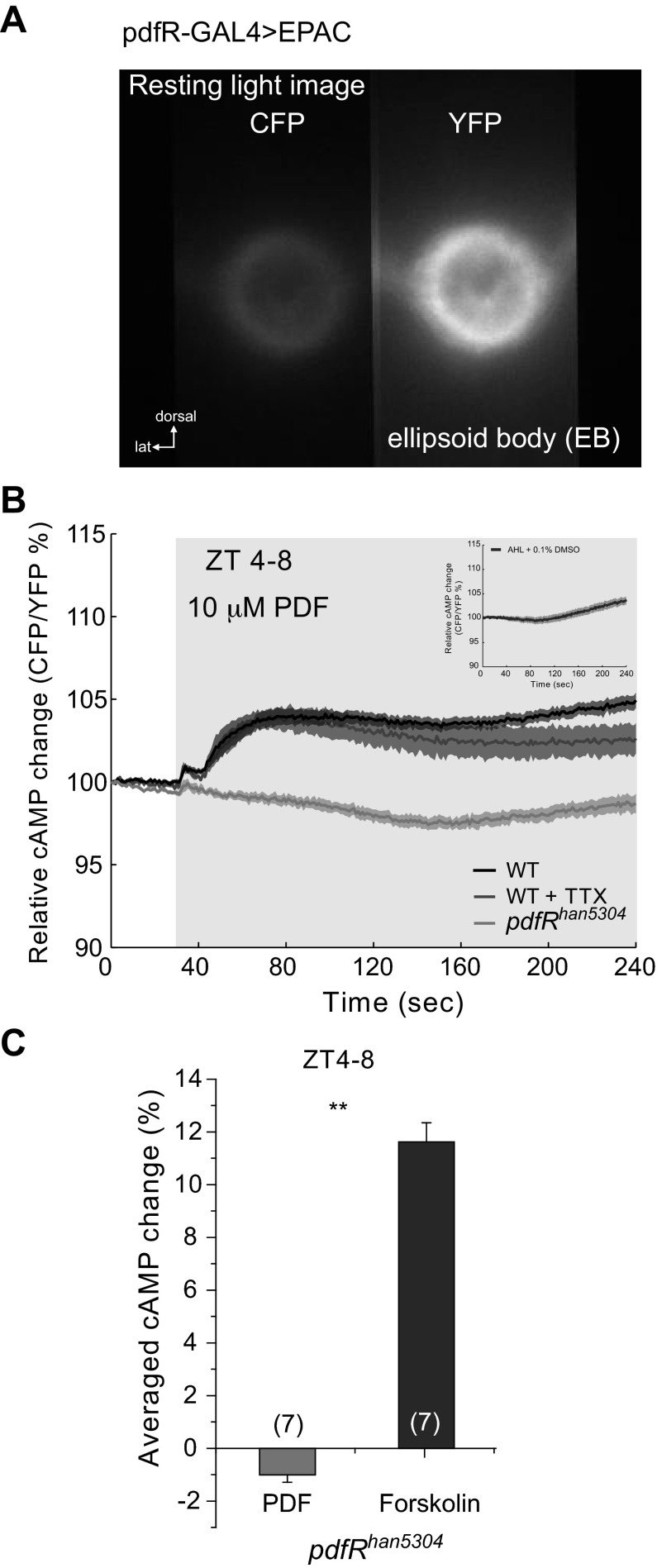
Pigment-dispersing factor (PDF) increases cAMP levels in ellipsoid body (EB). A: resting light image showing the expression of the UAS-Epac1-cAMPs (50AII) driven by pdfR-Gal4 in the EB. Left channel shows the cyan fluorescent protein (CFP) emission, and right channel shows the yellow fluorescent protein (YFP) emission, as is seen by using a splitter. EPAC, exchange protein directly activated by cAMP; lat, lateral. B: relative cAMP change, measured as the CFP/YFP percentage change. Average responses of EB neuropil of wild-type (WT) flies to the perfusion of 10 μM PDF (black trace) and 10 μM PDF + 1 μM TTX (dark gray trace). When pdfRhan5304 mutant flies were perfused with 10 μM PDF, no response was observed (light gray trace). Light gray box on figure represents the duration of stimulation. See text for statistical analysis. Inset: figure shows the response to the vehicle [artificial hemolymph-like (AHL) + 0.1% DMSO]. ZT, zeitgeber time. C: average data using the area under the curve of response of pdfRhan5304 mutants to 10 μM PDF as shown in B. As a control, 10 μM forskolin was perfused onto pdfRhan5304 brains. Numbers in parentheses represent the number of preparations for each condition (1-way ANOVA, **P < 0.0001). Data are expressed as means ± SE.