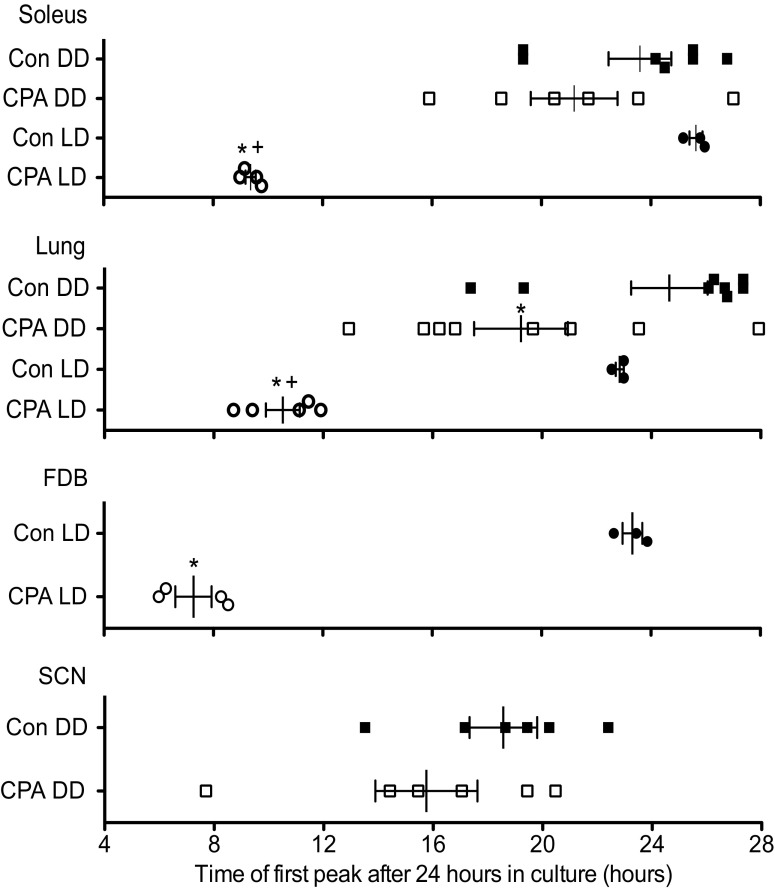
Fig. 5.
Effects of CPA and DD on the phases of the peripheral and central molecular clocks. Phase plot of first peak of PER2::LUC bioluminescence from cultured explants after 24 h in culture. The phases of PER2::LUC bioluminescence rhythms in the soleus, FDB, and lung were significantly shifted following exposure to CPA alone (compare control LD and CPA LD). When mice were exposed to 2 wk in DD following CPA, only the molecular clock in the lung remained significantly shifted (compare control DD and CPA DD). The phase of PER2::LUC bioluminescence rhythm in the lung was significantly shifted from controls in both the CPA DD and CPA LD groups, and there was a significant difference between the CPA group that was in DD from that cultured immediately following CPA (CPA LD). There was no significant interaction between group (CPA or control) and lighting condition (LD or DD), except in the rhythm expressed by the soleus. In the soleus muscle, there was no significant difference between CPA DD and control DD; only the CPA LD group was significantly different from control LD; however, CPA LD was still significantly shifted from CPA DD. Values are means ± SE (control DD, n = 8; CPA DD, n = 8; control LD, n = 3; CPA LD, n = 5). Not all tissues from each mouse could be used for analysis due to tissue culture survival. *Significant difference compared with control within lighting condition (P < 0.05). +Significant difference between CPA DD and CPA LD (P < 0.05; Student's t-test for FDB and SCN, two-way ANOVA with post hoc Bonferroni for soleus and lung).