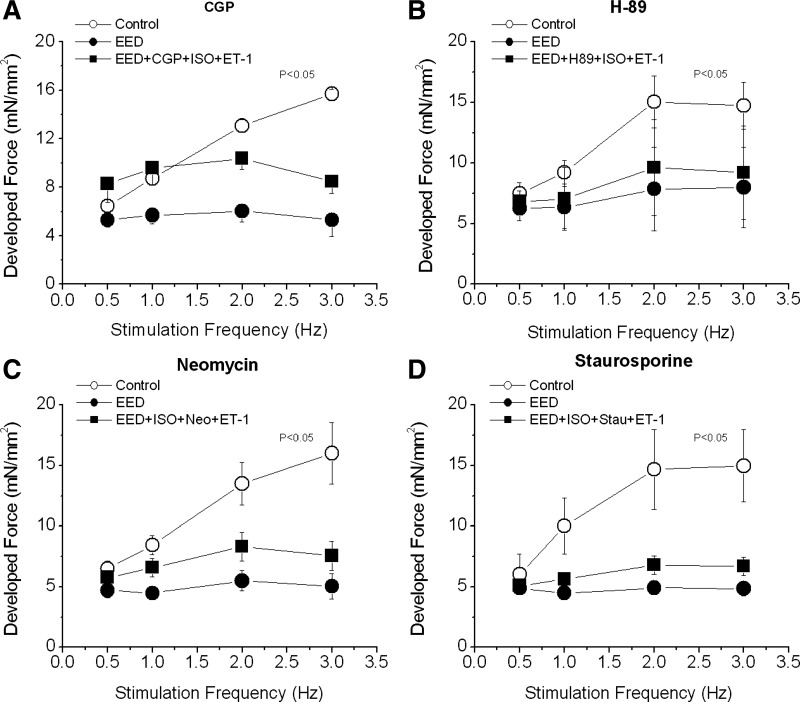
Fig. 8.
Effect of adrenergic, PKA, PKC, and PLC blockade on the FFR. FFR was measured in intact trabeculae (control) and in EED trabeculae. A and B: EED trabeculae were treated with CGP (2 μmol/l), a β1-adrenergic blocker (A), or H-89 (1 μmol/l), a PKA inhibitor (B), for 20 min after the endocardial endothelium was selectively damaged. Then ISO (0.1 nmol/l) and ET-1 (20 nmol/l) were added. C and D: EED muscles were treated with ISO (0.1 nmol/l) for 15 min followed by neomycin (Neo; 10 μmol/l), a PLC inhibitor (C), or staurosporine (Stau; 10 nmol/l), a PKC inhibitor (D), for 15 min. Then ET-1 (10 nmol/l) was added for 20 min. P < 0.05, control vs. other groups by multivariate ANOVA; n = 3–5 in each group.