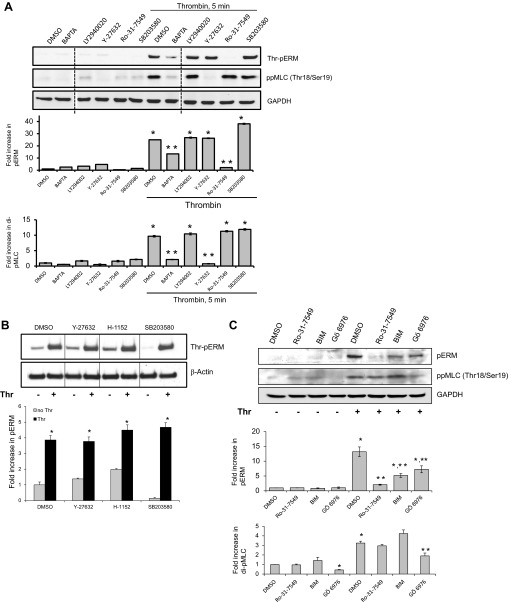
Fig. 3.
Thrombin-induced ERM phosphorylation requires activation of PKC. HPAEC were pretreated with either control vehicle or the following inhibitors: PKC inhibitors Ro-31-7549 (10 μM, A and C) for 30 min, bisindolylmaleimide (BIM, 1 μM, C) for 30 min, Go 6976 (1 μM, C) for 1 h, Ca2+ chelator BAPTA-AM (25 μM, A) for 1 h, p38 kinase inhibitor SB203580 (20 μM, A and B) for 30 min, Rho kinase inhibitors Y-27632 (10 μM, A and B) for 1 h and H-1152 (3 μM, B) for 1 h, phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitor LY294002 (10 μM, A) for 1 h. EC were then stimulated with EBM-2 medium alone or thrombin (0.5 U/ml) for the indicated time. Phosphorylation of ERM proteins and myosin light chain (MLC) were analyzed by immunoblotting of cell lysates with phospho-ERM (as in Fig. 2) or di-phospho-myosin light chain kinase (di-phospho-MLC) (Thr18/Ser19) specific Abs. GAPDH or β-actin Abs were used as a normalization control. Rearranged lanes from the same blot are outlined by vertical dotted line. Results of scanning densitometry of Western blots are shown as fold changes of ERM or MLC phosphorylation relative to vehicle treated EC stimulated by thrombin. Results are representative of 3–6 independent experiments. Values are means ± SE. *Significantly different from cells treated with vehicle (P < 0.05); **significantly different from cells stimulated with thrombin (P < 0.05).