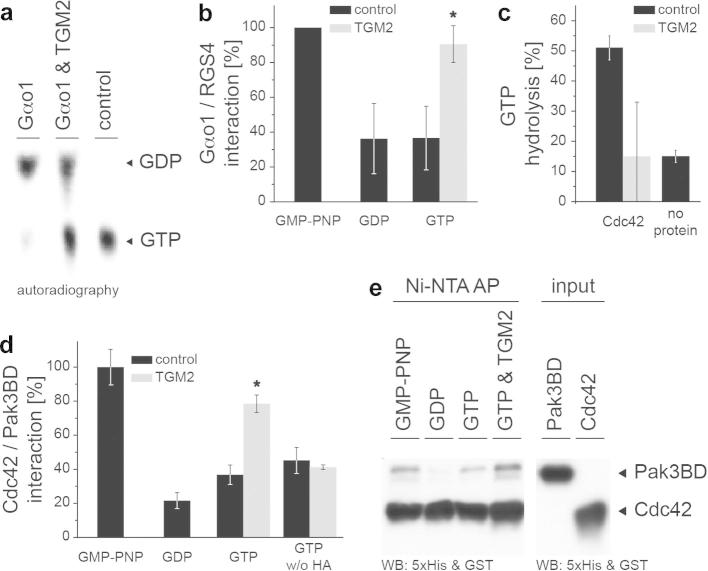
Fig. 3.
Histaminylated GTPases Cdc42 and Gαo1 show increased effector binding and decreased GTP hydrolysis. (a) Histaminylation of G proteins prevents GTP hydrolysis. Thin layer chromatography followed by autoradiography of [α-32P]-GTP incubated with native Gαo1, histaminylated (TGM2 exposed) Gαo1, and buffer. (b) Histaminylation stabilizes a Gαo1/RGS4 complex. 6×His-Gαo1, or TGM2/HA-exposed 6×His-Gαo1, was loaded with GMP-PNP, GDP and GTP and incubated with 2 μM GST-RGS4. The complex was immunoprecipitated (n = 5) and analyzed densitometrically. ∗p < 0.05. (c) Histaminylation of the Rho GTPase Cdc42 prevents GTP hydrolysis. 6×His-Cdc42 was exposed to TGM2/HA or HA alone, loaded with [γ-32P]-GTP, and GTP hydrolysis was induced by addition of MgCl2 and 0.2 μM p50RhoGAPΔ. After filtration, [γ-32P]-GTP was quantified using scintillation. (d, e) Histaminylation stabilizes a Cdc42/Pak3 complex. (c) 6×His-Cdc42 was pre-loaded with GMP-PNP, GDP and GTP, and incubated in multiwell plates with immobilized GST-Pak3BD in the presence of 0.2 μM p50RhoGAPΔ. Binding of 6×His-Cdc42 was strongly enhanced when the protein was pre-incubated with TGM2 and HA. (n = 3) ∗p < 0.05. (d) Pulldown of 40 nM GST-Pak3BD with 6 μM 6×His-Cdc42 pre-treated with GMP-PNP, GDP, GTP and GTP + TGM2/HA.