Figure 4.
CDK6 Regulates NPM-ALK-Induced Disease Progression
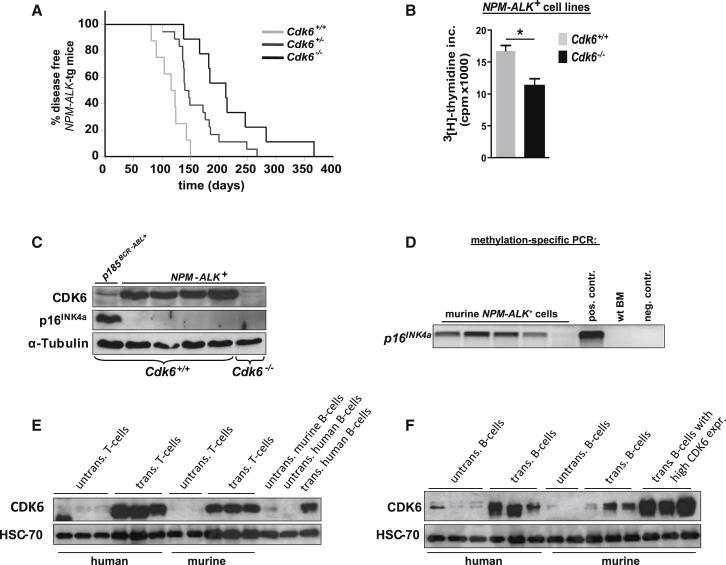
(A) Cdk6+/+, Cdk6+/−, and Cdk6−/− mice crossed with NPM-ALK transgenic (tg) mice developed a T cell lymphoma after several weeks (n ≥ 8; mean survival 120 [Cdk6+/+], 143.5 [Cdk6+/−], and 212 [Cdk6−/−] days; ∗∗p = 0.001).
(B) [3H]thymidine incorporation of NPM-ALK-transformed Cdk6+/+ and Cdk6−/− cells (n ≥ 3; ∗p = 0.009).
(C) Immunoblot for CDK6 and p16INK4a of NPM-ALK-transformed Cdk6+/+ and Cdk6−/− cells.
(D) Methylation-specific PCR of a part of the p16INK4a promoter CpG island in NPM-ALK-transformed murine cells. The visible PCR product indicates the presence of methylated alleles. wt BM, bone marrow of a healthy mouse; pos. contr., control for methylated samples; neg. contr., control for unmethylated samples.
(E) Immunoblot for CDK6 of untransformed human T cells (three individually derived samples), human T-lymphoid leukemic cell lines (Sudhl1, CCRF, PEER), untransformed murine T cells (two individually derived samples), murine Cdk6+/+ NPM-ALK-transformed cells, untransformed murine B cells, untransformed human B cells, and human B-lymphoid leukemic cell lines (SUP-B15).
(F) Immunoblot for CDK6 of untransformed human B cells (three individually derived samples), human B-lymphoid leukemic cell lines (SUP-B15, RL-7, JVM2), untransformed murine B cells (two individually derived samples), murine Cdk6+/+ p185BCR-ABL-transformed cells (three individually derived cell lines), and murine Cdk6+/++Cdk6 p185BCR-ABL-transformed cells (three individually derived cell lines).
Error bars indicate the mean ± SEM. See also Figure S4.