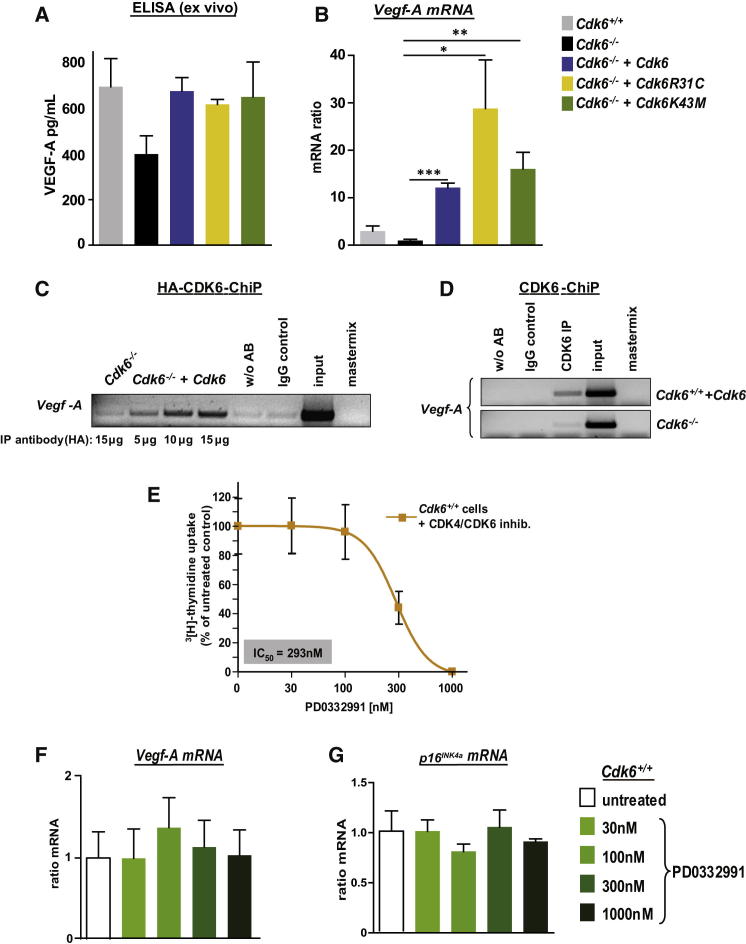
Figure 6.
CDK6 Regulates Transcription of the Pro-Angiogenic Factor Vegf-A
(A) Ex vivo VEGF-A protein levels (pg/ml) of the subcutaneous tumors (see Figures 5A–5C) were analyzed with an ELISA experiment (n = 3).
(B) Relative Vegf-A mRNA levels of indicated cells were analyzed by qPCR. The fold change compared to Cdk6−/−Vegf-A mRNA level is shown (n ≥ 4; Cdk6−/− versus: Cdk6−/−+Cdk6, ∗∗∗p < 0.0001; Cdk6−/−+Cdk6R31C, ∗p = 0.03; Cdk6−/−+Cdk6K43M, ∗∗p = 0.004).
(C and D) ChIP assays were performed on (C) Cdk6−/− and Cdk6−/− cells expressing an HA-tagged CDK6 using different amounts of an anti-HA-antibody as well as on (D) Cdk6−/− and Cdk6+/++Cdk6 cells using an anti-CDK6-antibody. PCR was performed to detect the Vegf-A promoter sequence.
(E) Dose-response curve of Cdk6+/+ p185BCR-ABL-transformed cells treated 24 hr with the CDK6/4 inhibitor PD0332991 (n = 3).
(F) Vegf-A mRNA levels of Cdk6+/+ p185BCR-ABL-transformed cells (n = 3) treated 24 hr with 0, 30, 100, 300, and 1000 nM PD0332991 were analyzed by qPCR. The fold change compared to untreated Vegf-A mRNA levels is shown.
(G) p16INK4a mRNA levels of Cdk6+/+ p185BCR-ABL–transformed cells (n = 3) treated 24 hr with 0, 30, 100, 300, and 1,000 nM PD0332991 were analyzed with qPCR. The fold change compared to untreated p16INK4a mRNA levels is shown.
Error bars indicate the mean ± SEM. See also Figure S6.