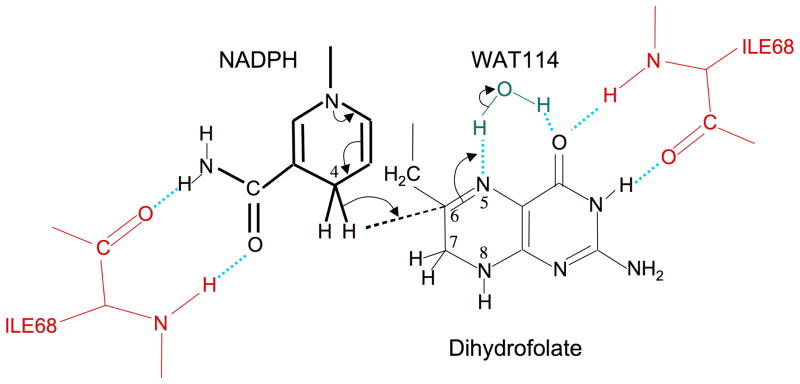
Figure 7.
Enzyme-substrate interactions and catalytic mechanism. The enzyme exploits a subtle symmetry between the NADP+ cofactor and the DHF substrate by interacting similarly with the nicotinamide amide group in the first case, and the N3-O4 amide group of the pteridine. In both cases, a pair of hydrogen bonds is formed with the backbone carbonyl and amide groups of the Ile68 residues on chains A and D. As a result of these and other interactions described in the text, the relative positions of two ring systems are optimized for hydride transfer to C6. This transfer follows or is concerted with N5 protonation, presumably from WAT114. WAT114 is within hydrogen bonding distance of DHF O4, but is solvent accessible and does not otherwise appear to be specifically activated.